
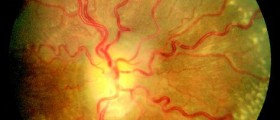
Glaucoma is not a single condition. It represents several eye disorders all of which are characterized by increased intraocular pressure (pressure inside the eye). Increase in intraocular pressure is detrimental for many eye organs, particularly the optic nerve. If it lasts for a certain period of time, increased intraocular pressure may easily cause loss of vision. In fact, glaucoma is reported to be one of the most common causes of blindness throughout the world.
Glaucoma - the Onset of the Disease
The aqueous humor is a watery substance that fills the inside of the eyeball (the front portion of the eye) and is in charge of many functions such as maintaining intraocular pressure and inflating the globe of the eye. Additionally, it nourishes avascular tissues of the eyes. Furthermore, the aqueous humor contains anti-oxidants and immunoglobulins, very powerful protectors.
There is a constant flow of the aqueous humor through the eye and if the amount of this fluid increases (suddenly or rapidly), a person is said to be suffering from glaucoma.
Major Subtypes of Glaucoma
Primary open angle glaucoma is a chronic and progressive disease which develops as a consequence of blockage of the tiny (microscopic) drainage channels.
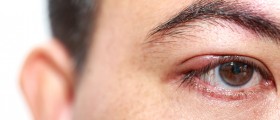
Primary angle closure glaucoma, on the other hand, is acute and severe disorder caused by sudden increase in intraocular pressure.
There is one more way to separated patients suffering from glaucoma. Namely, there are individuals with ocular hypertension. In them the pressure inside the eye is high each and every time it is measured. Still, the person simply does not develop any sign of glaucoma and there is also no damage to the optic nerve. Normal tension glaucoma is, however, a bit different because the pressure inside the eye is normal, bur there are noticeable signs of damage to the optic nerve.
Apart from the mentioned, glaucoma may occur as a complication of certain inflammatory disease of the eye such as uveitis, iritis and some eye surgeries or is a side effect of some medications (most commonly cotricosteroids). Treatment for Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma
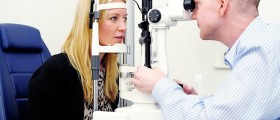
Treatment for glaucoma must be prompt and quickly reduce intraocular pressure. This is achieved by eye droops or medications administered orally and sometimes even intravenously. The condition may be also treated surgically.
Systemic medications prescribed to patients suffering from glaucoma are carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Laser treatment includes cutting a hole in the colored part of the iris. The hole allows excess of the aqueous humor to be drained. Surgical treatment (filtering microsurgery) also includes making a drainage hole, but this time the hole is created with a surgical tool.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...