
Eye Pressure
High blood pressure in the eyes,or as medically termed “ocular hypertension”, is the case of elevated eyepressure which is not accompanied by loss of vision or damage of the opticnerve. It is not a disease but rather a consequence of some underlying eyecondition, which is why people with increased eye pressure should be checkedregularly for potential ocular diseases, such as glaucoma. The eyes produce the fluid whichis then drained out of the eye through drainage channels, but in case of ocularhypertension, there is a failure in the functioning of drainage channels, sothe fluid stays inside the eye thus raising the eye pressure. Although nothingcan be done to prevent ocular hypertension, regular eye examinations reduce therisk of developing into a glaucoma, a condition combining raised eye pressure,vision loss and optic nerve damage. People older than 40, women aftermenopause, black people who have thinner corneas, those with primary open-angleglaucoma and those with pigment dispersion syndrome are risk groups for ocularhypertension.One in 10 people affected byraised eye pressure will develop glaucoma after 5 years, but medication andlaser surgery can lower the pressure in the eyes thus reducing the risk ofglaucoma by 50%.
Another eye defect that may result from the ocularhypertension includes retinal vein occlusion, the condition leading to visionloss because the veins in the retina become blocked. This affects less than 5%of people with raised eye pressure and can be prevented by keeping the pressurebelow 25 mmHg, which is especially advised to people over the age of 65.
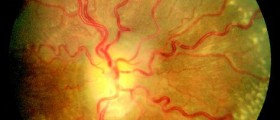
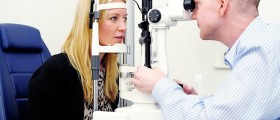
Since people with raised eyepressure usually experience no symptoms, regular visits to the ophthalmologists areadvised to check for any damage that might be done to the optic nerve. Ophthalmologistsuse numerous methods to establish the cause of ocular hypertension and checkfor glaucoma, and there are several tests that may be included in theexamination. A visual acuity test is performed to check how well a person seesobjects by reading letters from the other side of the room. Side (peripheralvision) is assessed by way of the visual field test, while gonioscopy is usedto see if the drainage channels are open, narrowed or closed. Fundus (back ofthe eye) photographs are made to check for optic nerve damage, and pachymetrymeasures the thickness of a cornea. A special microscope called slit lampexamines the changes in the front of the eye.
In order to prevent theprogression of ocular hypertension to glaucoma, eye pressure needs to belowered, and in this purpose medication in the form of eye drops haseffectively been used. Sometimes the patients are just observed regularlywithout any medical treatment, but in cases of haloes, pain, blurred vision andcontinuous raise in eye pressure, medication has to be prescribed. If medicinesfail, surgery might be required to lower the pressure inside the eye. However,early detection reduces the risk of glaucoma and for most people the use ofmedicines is all it takes to take care of the condition.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...