
Myopia, also known as nearsightedness, together with hyperopia and astigmatism belongs to a group of eye disorders called refractive errors. All of them are closely connected with inadequate refraction of light that enters the eye and subsequent problems with vision.
In case of myopia the affected individual faces difficulty seeing distant objects while at the same time he/she can easily see objects close to the eye and successfully perform activities such as reading or sewing.
It is estimated that myopia affects one-third of all population in the United States which makes it quite a common refractive error. Also, the number of newly diagnosed cases has significantly increased. What are Symptoms and Signs of Myopia?
This refractive error typically leads to eye strain, headaches and fatigue, especially after driving or playing some sports. The affected individual may also squint. This is frequently reported among children, who are because of this sign taken to the doctor.
People who are already diagnosed with the condition and have prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses may also experience the previously mentioned problems. In such case, they are due to consult their ophthalmologist and check their vision which might have deteriorated.
Myopia Pathophysiology
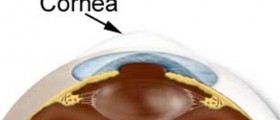
In people suffering from myopia the problem develops as a consequence of specific anatomical changes of the eye. Namely, the eyeball of these individuals is slightly longer. As a result, light rays do not focus on the retina (where they are supposed to) but instead they focus somewhere in front of the retina. This is the reason why patients cannot see clearly distant objects.
Treatment for Myopia
This refractive error is easily brought under control. The patients is either prescribed eyeglasses or contact lenses or he/she may opt for surgical correction.
Eyeglasses/contact lenses must be worn only when one looks far into the distance like when driving, watching movies etc.
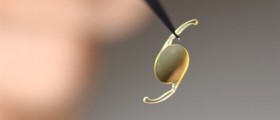
Refractive surgery is an excellent solution for these patients because it completely eliminates the need for eyeglasses or contact lenses. PRK surgery includes removal of a layer of the corneal tissue. This way the cornea gets flattened. As a result, light rays are focused onto the retina, where they should be. During LASIK surgery, on the other hand, a surgeon cuts a flap through the top of the cornea, removes some corneal tissue and finally, the flap is returned to its original place.
For people who are not willing to undergo surgery there is one more treatment option. This is a non-surgical procedure with specially designed contact lenses which slowly reshape the cornea over time. Once these contact lenses are removed the cornea retains the new shape for some time and one can see clearly. The best effects are achieved if such contact lenses are worn at night.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...