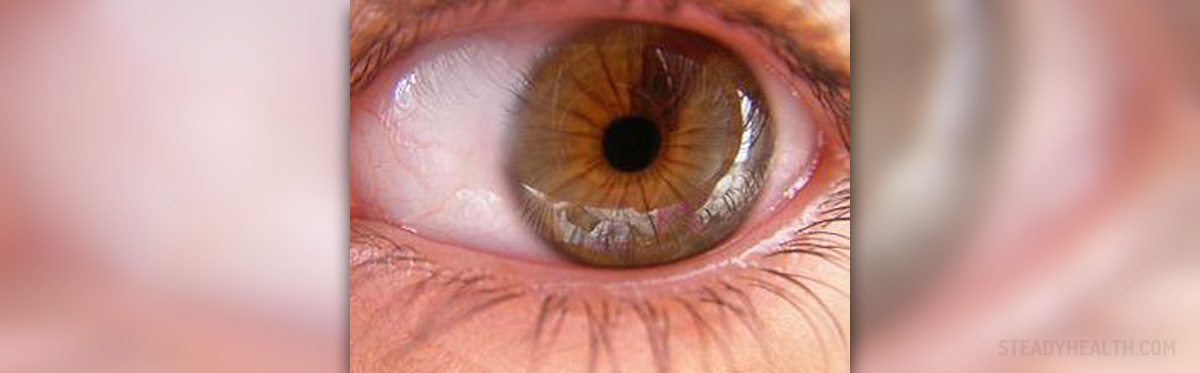
LASIK eye surgery is a type of refractive surgery used to correct various vision problems such as myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. Myopia is characterized by image that is out of focus when looking at a distant object but comes into focus when looking at a close object. Hyperopia, on the other hand, causes difficulties focusing on near objects. Astigmatism is characterized by blurred vision resulting from the inability of the optics of the eye to focus a point object into a sharp focused image on the retina. LASIK eye surgeries correct all of these problems, and they are becoming increasingly popular all around the world, including the United Kingdom. According to the official statistics, around 100,000 people in Britain are having laser eye surgery every year.
How it works?
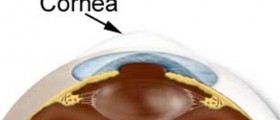
Lasik, the most commonly performed refractive surgery procedure, is a short name for "laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis." This surgical procedure stands out from the rest of the vision correction methods because it usually includes less pain and helps the patient achieve a good vision only one day following the surgery. The procedure is performed by small instrument, known as microkeratome, containing a disposable blade that surgeons use to cut the cornea. Sometimes surgeons will use laser instead of microkeratome to create a thin flap in the cornea and remove some corneal tissue underneath. The goal of the procedure is to reshape the cornea so that it works better to focus the light into the eye. As a result, the vision is clearer than before.
What to expect?
Most patients will notice dramatic improvement in vision right away. For others, the vision will gradually improve over a couple of days or weeks. The outcome usually varies from one patient to other but in general, people can expect to achieve 20/20 or better vision with LASIK. A small portion of patients will need glasses or contact lenses even after the surgery. However, their prescription level is expected to be much lower than before the surgery. In very rare cases, people may experience worsening of the eyesight over time. This phenomenon is known as “regression” and it is usually treatable with an additional surgery.
After the surgery, patients will need to have a lot of rest and use prescribed medication. Typically, patients are able to continue normal day-to-day activities the next day. However, if it is possible, patients should take a couple of days of rest and avoid any kind of physical effort for up to a week.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...