Myopia, also known as nearsightedness or shortsightedness is a refractive defect of the eye. Refractive defects occur as errors in the focusing of light by the eye. As a result, people affected with myopia will see the image out of focus, when looking at distant objects. At the same time, these individuals will have clearly focused image when they are looking at close objects. Changes in the focus are occurring when parallel rays of light that enter the eye produce image focus in front of the retina when accommodation is relaxed. Therefore, the light does not directly focus on the retina, which is positioned at the back of the eye. Therefore, the light entering the eye is focused incorrectly, which makes the distant objects appear blurry.
Causes of myopia
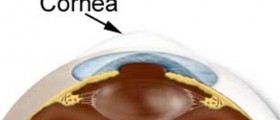
As already mentioned, myopia occurs when the physical length of the eye is greater than the optical length. Normally, people are able to see clearly, when the frontal part of their eye refracts the light and reflects it to the back of the eye, a portion known as the retina. In most cases, nearsightedness affects otherwise healthy people, with no other underlying eye problems. It affects both males and females, and it may sometimes run in the families. However, according to the most recent studies, environmental factors seem to play the most important role in developing myopia. Increased hours spent focusing to close up, such as while reading or sitting in front of the computer, are positively associated with myopia. People with myopia also tend to have a bit larger and longer eyeballs, which is possibly associated with intensive focusing in the young developing eyeball. The incidence of myopia greatly varies with age, country, sex, ethnicity, occupation and other factors. The prevalence of myopia is highest in China, and its incidence apparently increases with the level of education. Therefore, the most common explanation for myopia is near work.
Diagnosis of myopia
Myopia is diagnosed during an eye exam by an ophthalmologist, optometrist or orthoptist. Doctors may also use a phoropter, which is an instrument containing different lenses used for refraction of the eye during sight testing. The purpose of this test is to measure the extent of individual’s refractive error and establish the most accurate eyeglass prescription.
Management of myopia
People affected with myopia have many treatment options available. In most cases, these patients will wear eyeglasses or contact lenses, and some of them may even opt for refractive surgery. The most popular type of surgery for myopia is LASIK, which is a corrective procedure used to reshape the cornea and improve the vision.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...