
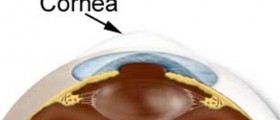
Keratoconus is a progressive eye disorder characterized by the change of the normal shape of the cornea, which instead of being dome-shaped becomes more like a cone. The condition occurs due to paraxial stromal thinning and weakening of the cornea. The previously mentioned changes are blamed for corneal surface distortion. The condition affects both eyes, is not associated with inflammation of any kind and eventually leads to problems with vision, most commonly astigmatism and myopia.
Keratoconus Treatment Options
Keratoconus can be treated conservatively or surgically. Ophthalmologists first opt for conservative treatments and only if all of these fail to provide with desirable results, a patient is recommended surgery.
Keratoconus Medical Care
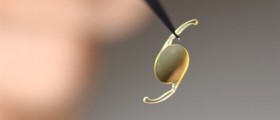
Rigid contact lenses are a cornerstone of conservative keratoconus treatment. Initially, when there is no significant distortion of the cornea, patients are usually prescribed eyeglasses or spherical/toric soft contact lenses. More advanced cases of keratoconus require rigid contact lenses and once these cannot be worn any more one can opt for hydrogel contact lenses, piggyback contact lenses or scleral contact lenses. Wearing contact lenses is in such patients closely connected with intolerance, sometimes allergic reactions and corneal abrasion. Furthermore, the organ may be affected by neovascularization which only leads to additional problems.
There is one more non-invasive procedure still not approved by the FDA. It is called collagen cross-linking (CXL). It seems to increase the rigidity of the cornea and includes using UVA light and a photomediator (riboflavin). However, long-term biomechanical effects of this treatment are yet to be studied so it is still not widely accepted.Keratoconus Surgical Care
The abnormal shape of the cornea eventually requires surgical correction. Sometimes patients may benefit from removing central nodular scars by shaving the surface of the organ. This procedure is known as superficial keratectomy. It is performed with a blade and may also be successfully done by applying the excimer laser. Superficial keratectomy increases lens tolerance and is highly efficient against corneal abrasion. It also postpones the need for transplantation of the cornea.
Furthermore, moderate cases of keratoconus are treated with intrastromal corneal rings. They also increase lens tolerance. Lamellar keratoplasty is another surgical procedure efficient against keratoconus.
Finally, the most severe cases of keratoconus require corneal transplant penetrating keratoplasty (PKP). The results of this surgery are excellent and vision significantly improves. Some patients require only one graft, while others undergo repeated procedure. Even though surgery is successful patients may need to continue wearing contact lenses. After the surgery patents need to have regular check-ups because there is the risk of rejection, suture-related problems and several more complications.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...