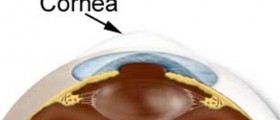
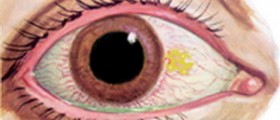
Keratoconus is an eye condition affecting the cornea, clear, central part of the front half of the eyeball. The cornea is under normal circumstances dome-shaped. In people suffering from keratoconus the cornea loses its original shape and becomes a bit distorted. In fact, this part of the eye starts to bulge outward like a cone.
Keratoconus Causes
In the majority of cases keratoconus is idiopathic, meaning that no underlying cause can be identified. Some experts believe that this is actually a hereditary condition, running in certain families. There are also people who believe that keratoconus develops together with some other conditions like allergies. Even though it may sound impossible, it may be that constant rubbing of the eye initiates keratoconus.
The condition starts in adolescence and is sometimes reported to occur in childhood. The bulging of the cornea progresses gradually, over several years. Once the cornea has significantly changed in shape, a person reports vision problems, most commonly distorted vision. In some people bulging may eventually stop, while in others it progresses unstoppably.
Both eyes may be affected at the same time. However, the extent of bulging may differ.
Keratoconus and Vision Damage
People mistake if they think that keratoconus leads to loss of vision. Still, excessive bulging may significantly interfere in focusing. This problem can be solved with eyeglasses and contact lenses.
Keratoconus may be dangerous if the person affected by it undergoes vision correction surgery, LASIK or PRK. So, individuals with keratoconus are strictly forbidden to undergo laser vision correction surgeries.
Diagnosing Keratoconus
Patients usually turn to their doctors once they experience sudden change of vision in just one eye, double vision while watching objects with the affected eye and distortion of near/far objects. Objects may appear of different color or shape and distant ones are usually blurred. Also, bright lights seem like they are surrounded by halos.
The easiest way to confirm keratoconus is by measuring the curvature of the cornea. This is achieved with several different instruments, one of which is called a keratometer. Today most ophthalmologist use computerized instruments in order to determine whether the cornea is abnormally shaped.
Keratoconus Treatment
Depending on the severity of keratoconus the ophthalmologist will recommend the most convenient treatment option. Initially, patients are prescribed a new pair of eyeglasses. If these fail to provide with desirable effects, a person may opt for rigid contact lenses. Finally, if all else fails, the patient may undergo surgical correction. Surgery for keratoconus includes removal of the old and distorted cornea and its replacement with a corneal transplant.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...