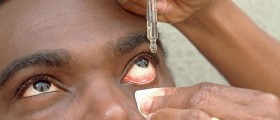
Eye medications
Eye medications are most commonly employed in order to treat problems such as infection, allergy, inflammation, and glaucoma. In some cases, it is also possible to use eye drops in order to dilate the pupils for diagnosis. The ocular surface can also be dyed in order to prepare for an examination of the eye. It is also common for eye drops to be used in order to numb the eye. To use eye drops or ointments correctly, make sure your hands are clean before doing so. Tilt back your head, look up, and gently pull the lower lid away from the eye. Make a pouch from the eye, and pour one drop of ointment into the pouch. Try to avoid touching the eye or eyelid with the packaging. Normally, it takes about five minutes for proper absorption of the eye drop to occur. Thus, it is advised to wait about five minutes before using any other eye medications.
Eye medications side effects
There are some potential side effects with regard to the use of eye medication. Such side effects include stinging, blurred vision, redness, and photosensitivity. If one is using corticosteroids, then one might experience glaucoma, infection, and cataracts as a result of their usage. Make sure to carefully stick to the course of medication advised by your doctor or health care provider. It is also rare but not unheard of for ocular decongestant drops to lead to the onset of sudden glaucoma. Over use of anesthetic eye drops can lead to damage occurring in the cornea. It is also possible that one might experience problems such as sweating, stomach cramps, and diarrhea. On rare occasions, serious symptoms and reactions can occur. This includes problems such as asthma, lowered blood pressure, loss of memory, loss of sex drive, and disorientation. It is particularly important for diabetics to exercise caution when undertaking the use of these types of medication, as low blood sugar levels can be hidden through the use of these medications.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...