
Esophageal cancer is closely connected with several bad habits, some medical conditions and a few more factors. This cancer is frequently reported in people who smoke and consume large amounts of alcohol, those suffering from gastroesophageal reflux diseases and Barrett's esophagus as well as obese people.
Esophageal Cancer and Smoking
There is a clear connection between the onset of esophageal cancer and smoking. In fact, there are two explanations, the first one related to direct effects of smoking and the second one associated with indirect effects of smoking.
First of all, while smoking an individual inhales the smoke containing many irritants and harmful chemicals. They act directly onto the superficial cells of the esophagus and may eventually cause damage to their DNA. If a person is a heavy smoker, such damage is highly likely to occur. This is a direct effect of cigarette smoke to esophageal epithelium. So, by reducing the number of cigarettes smoked per day or complete smoking cessation, a person may timely prevent damage to DNA material of esophageal epithelial cells and also prevent esophageal cancer form occurring.
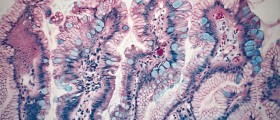
Secondly, smoking may increase the production of stomach acid. If stomach acid finds the way to enter the esophagus, it irritates its lining. Continuous or recurrent irritation of the esophagus by stomach acid is a potential trigger for Barrett's esophagus. This medical condition is characterized by a specific changes of epithelial cells of the esophageal lining. The presence of metaplastic epithelium in the esophagus is a huge risk factor for esophageal cancer. So, indirectly, by increasing the production of stomach acid, smoking may initiate the onset of certain medical conditions that eventually lead to esophageal cancer. Additional Problems
Another major contributor to esophageal cancer is heavy alcohol consumption. Unfortunately, many alcohol addicts are also smokers so the risk of developing esophageal cancer in them becomes even higher.
Smoking cigarettes is not only associated with esophageal cancer. This nasty habit is also blamed for a variety of other malignant illnesses among which the most commonly reported are lung cancer, laryngeal cancer, oropharyngeal cancer, pancreatic cancer, cancer of the nasal area as well as cervical, kidney and bladder cancer. Even certain types of leukemia effect more smokers than non-smokers.
So, by choosing to quit smoking, a person may rest assured that the chances for him/her to end up with some of the mentioned malignant tumors is reduced. The sooner the one quits smoking, the greater the chances not to end up with these malignant diseases are.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...