The esophagus is a muscular organ running from the mouth and ending in the abdomen where it continues with the stomach. The organ is approximately 10-13 inches long and its only function is to carry food and liquids to the stomach.
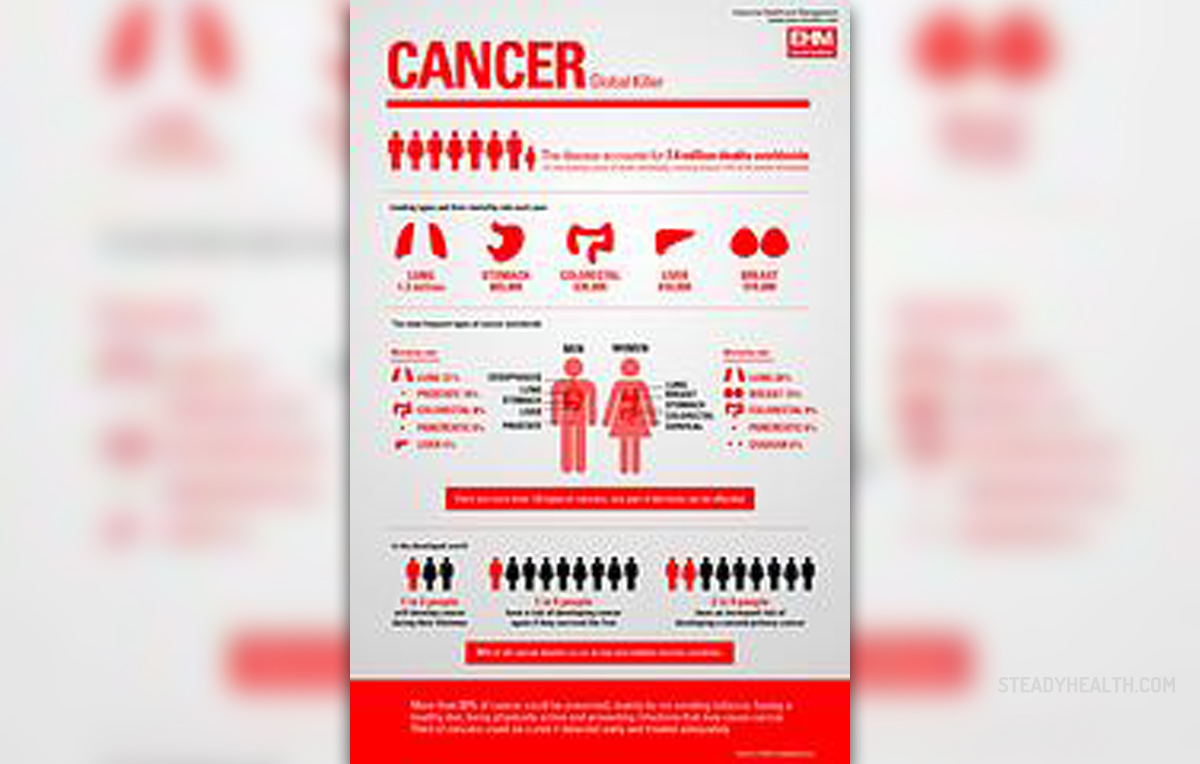
Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer is a malignant tumor originating from the innermost layer of the organ. Depending on the cells this tumor is made of it can be classified into adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. Both of these have huge malignant potential, soon penetrate the organ and easily spread to nearby as well as distant organs. Esophageal cancer is usually diagnosed when the disease has significantly progressed i.e. in later stages when the prognosis is not so good.
However, in people who are suffering from certain conditions affecting the upper gastrointestinal tract, especially those with Barrett's esophagus, the tumor may be diagnosed on time, in early stages, because such patients require regular endoscopic examinations.
Esophageal cancer is known to affect more people who smoke, drink a lot of alcohol as well as those who consume processed foods and foods preserved in lye such as lutefisk. Obesity is also related to higher incidence of esophageal cancer. All in all, once the cancer is confirmed, patients undergo treatment that may solely include surgery, radiation therapy or chemotherapy or a combination of these treatment approaches.
Esophageal Cancer Treatment Options
Doctors take stage of the disease as the most important factor when choosing the most efficient treatment for esophageal cancer. However, other factors are considered as well such as patient's age, comorbidities and the overall health of an individual. The goal is to eradicate the disease or if this is not possible, to reduce symptoms and signs patients have to deal with due to the presence of the tumor or metastases in the body. Terminal stage of the disease requires palliative treatment and care.
Surgery for esophageal cancer is the best treatment approach. It is performed in early stages of the disease. Patients either undergo esophagectomy or esophagogastrectomy. Even though there are many potential complications that occur after these two surgeries, they are still efficient because they remove the tumor from the body. After surgery patients may or may not undergo additional treatments.
Radiation therapy for esophageal cancer can be external or internal, performed prior to surgery (to shrink the tumor) or after surgery (to kill remnant tumor cells scattered around the operation site). Radiation therapy is usually combined with chemotherapy which increases the chance for elimination of greater number of cancer cells.
Chemotherapy is in a form of intravenous administration of chemotherapeutics, drugs that efficiently kill cancer cell, but may cause damage to healthy cells as well. Chemotherapy is in such patients recommended in case of advanced cancer, may be administered together with radiation therapy and can be also used before the surgery to shrink the tumor. Such treatment (as well as radiation therapy) has many side effects which are all successfully brought under control with symptomatic treatment.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...