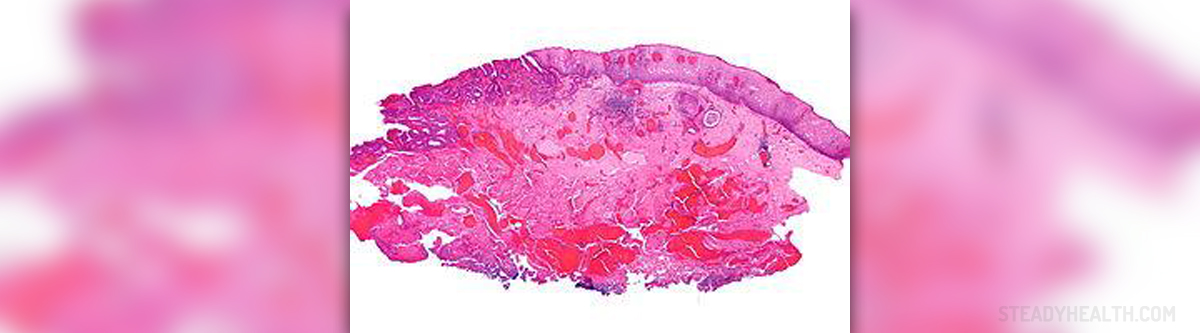
The esophagus runs from the throat to the stomach, connecting these organs and carrying the food which is to be digested. Esophageal cancer can appear in any part of the esophagus and affect any of esophageal cells, but it is frequently diagnosed in the lower portion this organ.
This is not a very common medical problem in the United States (US). However, many people all over the world, especially in Africa and Asia seem to be affected by this type of cancer. There are several types of esophageal cancer. Two most commonly diagnosed esophageal malignant changes are adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, while other types, such as lymphoma, sarcoma, melanoma, small cell cancer and choriocarcinoma are very rare. Caucasians living in the US are usually found to suffer from adenocarcinoma and African American people commonly develop squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus.
Know the Symptoms of Esophageal Cancer
Some patients suffering from any type of esophageal cancer may not have any symptoms, especially in early stages of cancer development. Others may notice swallowing problems (dysphagia, in medical terminology), frequent choking while eating and unintended weight loss. Many patients have reported fatigue, digestion difficulties, heartburn, as well as coughing and hoarseness. A person suffering from esophageal cancer (regardless the type) may experience pressure, burning or even painful sensations in the chest.
Any problems and symptoms resembling these mentioned above should be reported to your doctor. Routine screening of the esophagus is not common, probably because of endoscopy (diagnostic examination of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum) complications. Patients diagnosed to have Barrett’s esophagus, however, might be sent to endoscopy in some cases, because this problem is known as a precancerous change of the esophagus and might lead to esophageal cancer.
Be Informed about Causes and Risk Factors
Exact causes of esophageal cancer are not known, but doctors assume that mutation of DNA material leads to malignant changes of esophageal cells, their uncontrolled growth and division and development of esophageal cancer.
So far scientist have identified several risk factors which may contribute to formation of esophageal cancer, including heavy consummation of alcohol, smoking, chewing tobacco, drinking very hot drinks, as well as obesity. Eating very few fruits and vegetables or heavy consumption of food preserved in lye is also known to be linked to esophageal cancer.
Conditions such as achalasia (causes swallowing problems), bile reflux, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and Barrett’s esophagus also increase the chance for esophageal cancer. Radiation treatment of the chest or the upper part of the abdomen is also considered to be risk factor for esophageal cancer.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...