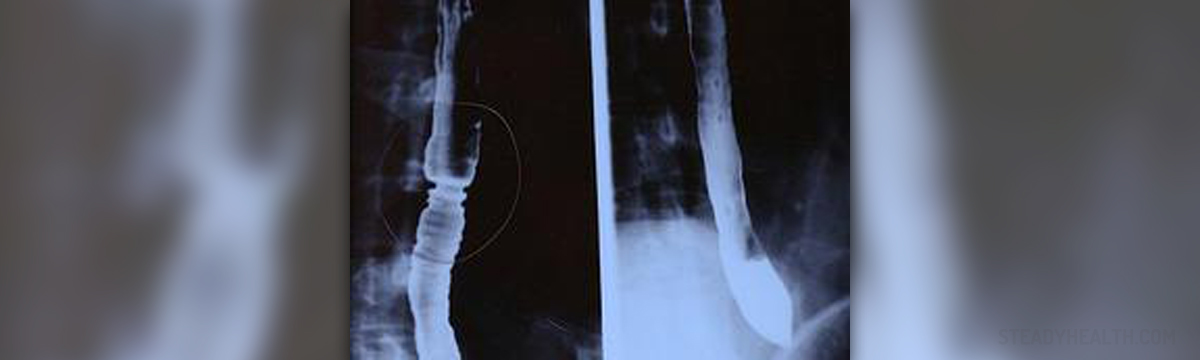
Esophageal cancer is a malignancy of the esophagus. The esophagus is an organ that consists of a muscular tube. Food passes through this tube from the pharynx to the stomach. This is why the word esophagus literally means "entrance for eating," as it is borrowed from the Greek word oisophagos. The esophagus is typically 25–30 cm long and connects the mouth to the stomach. Therefore, esophageal cancers usually lead to a difficulty swallowing, pain and other unpleasant sensations.
Types of esophageal cancer
There are a couple of different types of esophageal cancer. In most of the cases, esophageal cancer appears as a squamous-cell cancer. Squamous cells are found in the epithelium of the esophageal tissue. This superficial layer of the esophagus consists of flat, scale-like cells. Squamous cell cancer comprises for 90-95% of all esophageal cancer worldwide. Adenocarcinoma is also very common, and it occurs in 50-80% of all cases of esophageal cancer in the United States. Adenocarcinoma is a cancer of an epithelium that originates in glandular tissue. It affects the lining of the esophagus. Squamous cell carcinomas are generally associated with tobacco and alcohol consumption, while adenocarcinomas seem to be linked with a history of gastro esophageal reflux disease and Barrett's esophagus.
Signs and symptoms of esophageal cancer
Among the first symptoms of this disease, patients will usually notice difficulty swallowing and sometimes even pain with the swallowing. Difficulty swallowing typically appears first, and it may become associated with pain, as the cancer grows and the disease progresses. Patients will usually tolerate fluids and soft foods but swallowing of hard and bulky foods may be very difficult. In most cases, people will lose weight as a result of low appetite, poor nutrition and cancer activity. If the pain is present, it usually appears in the form of a heartburn that becomes even more pronounced with swallowing. Some patients may produce hoarse sounding cough, which results from the tumor affecting the recurrent laryngeal nerve, tumor affecting the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
When the normal swallowing reflex is disrupted, patients may start to experience severe problems with regurgitation of undigested food, nausea, vomiting and coughing. These individuals are at increased risk of aspiration pneumonia, which develops t develops due to the entrance of foreign materials in the bronchial three.
Patients should seek medical help upon the first symptoms of the disease. However, people usually do not pay a lot of attention to mild symptoms such as difficulties swallowing, and most of the cases of this severe disease, unfortunately, are diagnosed in the late stage.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...