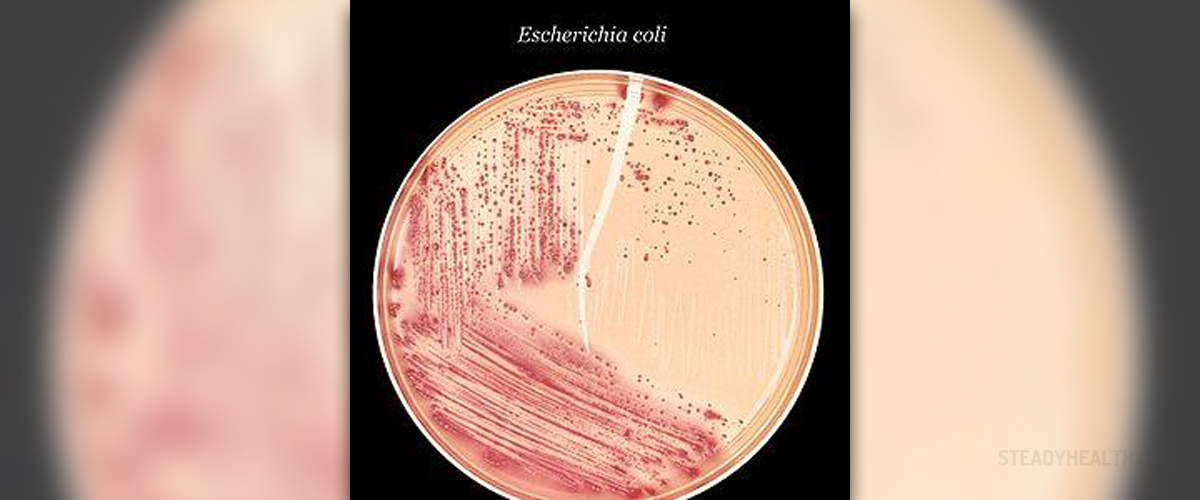
About E. coli
E. coli or Escherichia coli is a bacterial genus, named after Theodor Escherich who was the first to isolate the species of this genus.
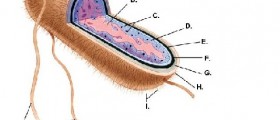
These bacteria are gram-negative and they live individually or in pairs. E. coli can be aerobic and anaerobic and both fermentative and respiratory. It is widely present around humans and it constitutes a great part of the human digestive tract.
Infections with E. coli are very common and they particularly affect the urinary tract. E. coli also causes traveller’s diarrhea, pneumonia and neonatal meningitis.
E. coli urinary tract infections
E. coli normally lives in the colon, a part of the intestinal flora, not causing any health issues. However, given the proximity of the rectum and the urinary tract, it can be very easy for the bacteria to migrate from the intestines to the urinary tract. They first inhabit the opening of the urethra and then they migrate upwards, causing infections as they multiply.
Urinary tract is the single most common site of E. coli infections and these bacteria are responsible for at least 90% of all urinary tract infections.
E. coli urinary tract infections are more common in sexually active women than in men. In almost half the cases the infection tends to reoccur. The infections include uncomplicated cystitis and urethrtitis, symptomatic cystitis, pyelonephritis, acute prostatitis and urosepsis.
E. coli infections of the urinary tract should be treated with antibiotics to kill the bacteria. It is also recommended to adopt certain lifestyle changes, such as better personal hygiene, better nutrition and less stress. Home remedies, such as cranberry juice, seem to help in some cases.
Symptoms of urinary tract infections
Even though urinary tract infections caused by E. coli can be asymptomatic, most people experience at least some of the symptoms. Most commonly, the symptoms include problems related to urination, such as tingling, burning or pain when urinating, frequent urge to urinate, especially during the night and even when the bladder is relatively empty.
A person suffering from a urinary tract infection may also feel tired, worn-out and achy. The pain may be generally present in the pelvic area all the time, not just when urinating. The urine may smell bad and become cloudy or with traces of blood in it.
In adults, fever is not common with E. coli infections of urethra or the bladder. It does, however, occur if the bacteria have reached the kidneys. On the other hand, children are more prone to fever during urinary tract infections, along with irritability, loss of appetite, loose bowels and incontinence.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...