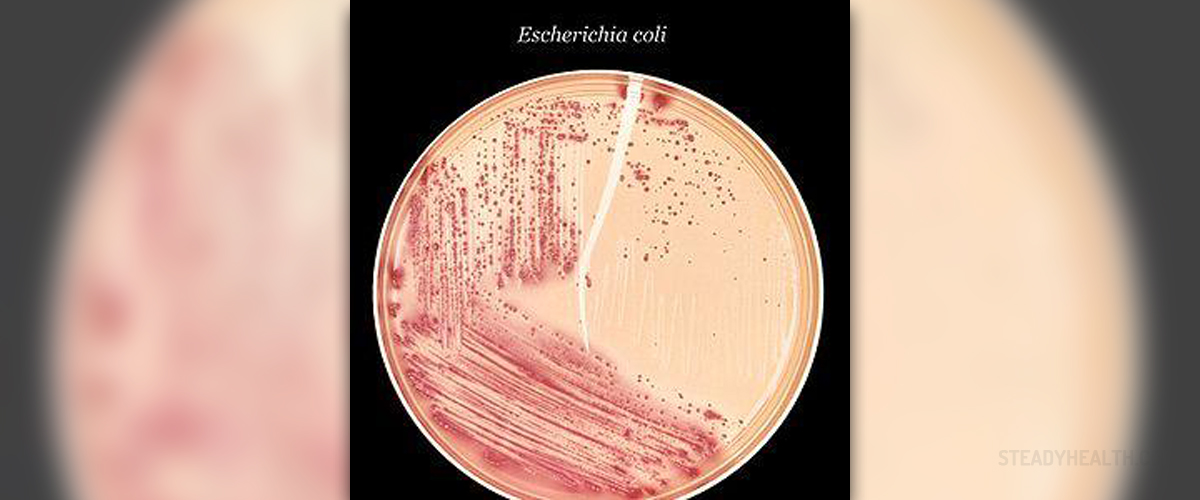
Escherichia coli is a Gram-negative bacterium, facultative anaerobe capable of producing flagella or pitti (hair-like structures), if necessary. This bacterium is normally found in the human intestine as well as the gastrointestinal tract of many animals. In such environment Escherichia coli is a normal inhabitant and is not a cause of any disease/infection. However, once the bacterium enters other organs, such are the urinary tract or even blood, it can start to multiple uncontrollably and initiate infections accompanied by many different symptoms and signs. Furthermore, certain strains of E. coli are culprits of poisoning and persistent diarrhea. Such strains are known as enterovirulent E. coli strains.
The first E. coli was found and isolated in 1885 by T.Escherich, hence the name of the bacterium. Experts have managed to isolate around 700 serotypes of Escherichia coli.
Escherichia Coli and UTI
According to National Institute and Digestive and Kidney Disease (NIDDK) E. coli is actually the major contributor to urinary tract infections in people living in the United State. Urinary tract infections (UTI) are frequently reported in both genders (women predominantly). The very infection usually affects the bladder, urethra or both and may easily spread to upper parts of the urinary tract, causing pyelonephritis (kidney inflammation). The symptoms of UTI caused by Escherichia coli are actually the same as symptoms of urinary infection caused by other bacteria. In all cases there is abnormal presence of bacteria in urine which is responsible for discomfort and all the negative sensations patients have to deal with.
Escherichia Coli Urinary Infection Symptoms and Signs
Dysuria is the leading symptom of E. coli UTI. This is burning or stinging pain associated with urination. Pain patients complain about may also occur when one is not urinating and is then located in the lower portion of the abdomen, right behind the pelvic bone. Patients may additionally complain about pain in the lower back and flank area.
As for fever, it is present in children all the time. In adults fever only accompanies inflammation of the kidneys, i.e. occurs once the infection spreads from lower portions of the urinary tract onto the upper parts.
Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea may occur in case E. coli infection affects infants and young children. Association of such symptoms with infection in adults is not a common scenario.
Urine contains plenty of bacteria. Their presence and the presence of their products gives urine characteristic smell (a strong, foul odor). Also, the very appearance of urine changes so there may be traces of blood and it generally loses it natural transparency. Urine analysis conforms the presence of different amounts of blood, white blood cells, proteins and confirms the presence of bacteria. The more blood there is in the urine, the darker the urine appears.
















Your thoughts on this
Loading...