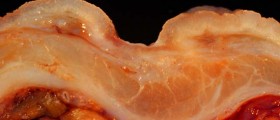
Duodenal ulcers are shallow sores affecting the surface of the duodenum. They develop as a consequence of entrance of stomach acid into the duodenum and irritation of the organ's mucous membrane. It is estimated that duodenal ulcers affect approximately 10% of all adult people. The lesions in the duodenum may be of different size.
Diagnosing Duodenal Ulcers - Endoscopy
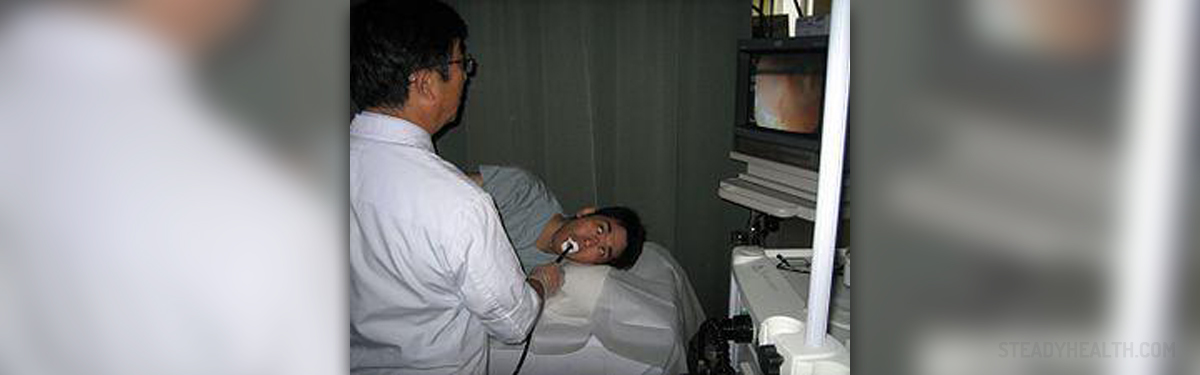
Endoscopy has become a procedure routinely performed in patients with suspected peptic ulcers in the duodenum. Double-contrast barium study is cheaper comparing to endoscopy, but it is of lower sensitivity. Endoscopy is unlike double-contrast barium invasive procedure that includes swallowing of a tube called endoscope, containing a tiny camera at the end. After reaching the duodenum, the camera visualizes the inside of the duodenum and easily confirms the presence of ulcers. The procedure also allows taking samples from the affected organ even though all duodenal ulcers are actually benign lesions.
Are There Any Limitations?
Although the procedure is sensitive in approximately 95% of cases, there is also chance that small peptic ulcers in the base of the duodenal bulb may be overlooked. Also, the procedure simply cannot be performed in case of the presence of obstruction of the gastric outlet and the proximal part of the duodenum.
Additionally, the same efficacy regarding depicting ulcers larger than 10 mm in size is achieved with double-contrast barium study. But double-contrast barium study is practically inefficient when it comes to small duodenal ulcers as well as recurrent ulcers affecting the already deformed duodenal bulb. Finally, only during endoscopy doctors may take tissue samples i.e. perform biopsy, if necessary.
Other Advantaged of Endoscopy regarding Duodenal Ulcers
Apart from being of great help in diagnosing duodenal ulcers, endoscopy is also very helpful because it allows small interventions at the very site of examination. Treatment of bleeding ulcers is only one example of many advantages of duodenal endoscopy.Duodenal Ulcers and Complications
It is estimated that 20-30% of all duodenal ulcers will eventually bleed. Endoscopic examination will be efficient in confirmation of 90% of all bleeding sites. The problem with detection of the site of bleeding may occur because there is a blood clot, food debris and granulation tissue at the base of the ulcer.
Scarring of the affected parts of the duodenum is associated with different deformities. Gastric outlet obstruction affects 10% of all patients ( two-thirds of all adults suffering from the disease). Apart from causing difficulties while performing endoscopy, obstruction is also a problem associated with food digestion/passability and may eventually require surgical correction.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/stomach-ulcer/diagnosis/
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003888.htm
- Photo courtesy of Yuya Tamai by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Endoscopy_training.jpg











Your thoughts on this
Loading...