
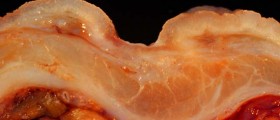
Bleeding ulcers, known as peptic ulcers, can be easily treated. However, the peptic ulcers are sometimes discovered when complications develop such as bleeding and rupture which requires immediate medical attention.
Causes of Bleeding UlcersPeptic ulcers are open sores in the lining of the stomach, duodenum or esophagus. They develop when digestive acids damage the walls of stomach or small intestine. Peptic ulcers are common condition that can be successfully treated.
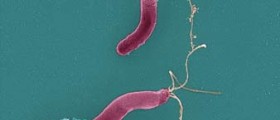
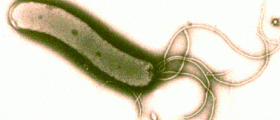
Bleeding ulcers occur due to two major causes. It can result from an infection with Helicobacter pylori in most of the cases. Other reason may be use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Aspirin, ibuprofen and naproxen. NSAIDs hinder ability of the stomach to produce mucus and bicarbonate and they also affect blood flow to the stomach and its defense mechanisms.
Other causes of bleeding ulcers can be lifestyle factors such as smoking, consuming alcohol, drinking caffeine and physical stress.
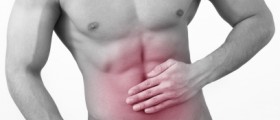
Symptoms of Bleeding UlcersA person may not have any symptoms of bleeding ulcers. Common symptoms include following: severe stomach pain that can last from several minutes to several hours, bloating, nausea, vomiting, tiredness and weakness. Sometimes there may be blood in vomit or in stool which has tarry or black appearance.
Bleeding Ulcer TreatmentDepending on the cause a doctor may choose different treatment for bleeding ulcer. If it is a result of H. pylori infection, a patient will have to take antibiotics. If bleeding ulcer is caused by NSAIDs a patient will have to discontinue the medication that has caused it and take some painkillers.
Endoscopy is commonly used for treating bleeding ulcers. Endoscopy is a procedure that uses small device called endoscope which allows stopping bleeding from ulcer by applying electricity, heat or small slips to coagulate the blood. Surgeon may also administer adrenaline or fibrin glue injections to reduce the risk of rebleeding. This procedure successfully treats bleeding in 90% of patients. Repeated endoscopy may be required in case that rebleeding occurs and the procedure is effective in 70% of patients.
Surgery is required when endoscopy cannot stop the bleeding. This treatment is the most successful for severe blood loss. During the procedure blood vessels are tied up and the ulcer is stitched close. Surgical options for treating bleeding ulcers include open surgery and laparoscopic technique.
Follow-up treatment for bleeding ulcers includes antibiotics for eliminating Helicobacter pylori infection. Proton pump inhibitors can be administered intravenously to promote the healing of bleeding ulcers and prevent bleeding that may start again later. Somatostatin is also sometimes given. It is a hormone that is used to prevent bleeding in cirrhosis but it also successfully treats continual bleeding of peptic ulcer and prevents rebleeding as well.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...