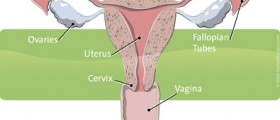
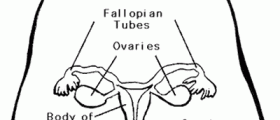
The uterus is a hollow organ located in the pelvic area, being a crucial part of the female reproductive system. This organ consists of three parts. The first one is the dome-shaped upper part called the fundus. From here, the fallopian tubes spread to the ovaries. The second part of the uterus is the middle part called the corpus. This part is a temporary home for the growing and developing fetus during pregnancy. Finally, there is the bottom part of the uterus, being narrow and providing a way to the vagina. This part is called the cervix.
Parts of the Uterine Wall
The wall of the uterus has layers which are made of different tissues. The inner layer of this wall is called the endometrium. When a woman reaches her fertile age, this lining of the uterus becomes thicker, making the body prepared for pregnancy. However, if the pregnancy does not take place, the thick layer gets expelled out of the body during menstrual cycles.
The second, outer layer of the uterus is called the myometrium. This lining is made of muscle tissue.
Facts about Uterine Cancer
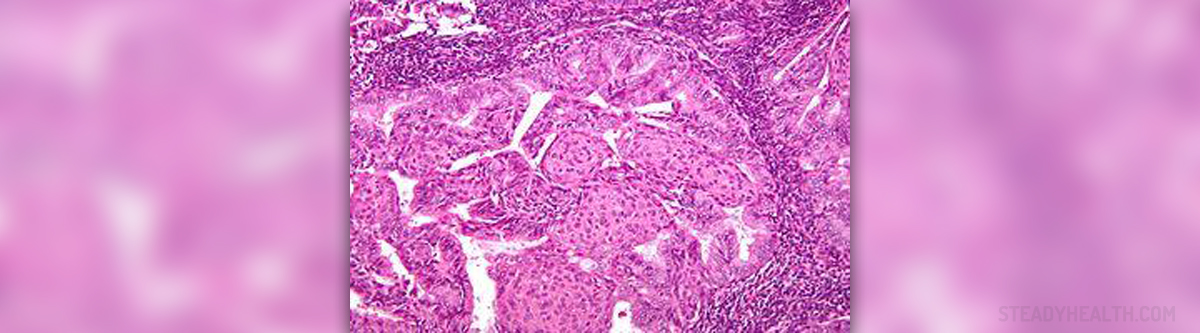
Once cancer affects this area, it initially appears in a single cell, being the smallest unit of every single part of our body. When cells are healthy they divide and create new cells, satisfying the needs of the body. If certain cells get damaged or old, they die and get replaced by new cells.
However, this process does not always go according to plan. Rather, more cells may get formed than it is necessary and old cells do not die in some situations. Then, these extra cells accumulate and form tumors which can be either benign or malignant. Benign tumors can be treated easily and do not cause harm while malignant ones are commonly referred to as cancers, being dangerous and potentially life-threatening.
While benign tumors do not spread or invade other tissues in the body, malignant ones do, making the whole situation worse unless timely treatment takes place. Also, malignant tumors tend to reappear even once they have been surgically removed.
Once cancer cells appear in the uterus, they can leave the tumor and spread to the lymph nodes and blood vessels, affecting the heart, the lungs, the bones or even the brain, leading to formation of new tumors and more malignant cells.
Vaginal bleeding, spotting or discharge are the first signs of uterine cancer. The bleeding may appear outside the menstrual cycle or during menopause. Painful urination and pain during sexual intercourse are additional symptoms of this condition. Finally, general pain felt in the pelvic area adds on to the list of signs.
Once you notice these signs, seek medical assistance immediately. Your doctor will perform physical, ultrasound, biopsy and other types of exams, establishing a diagnosis and suggesting the best possible treatment.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...