Defibrillator Implant
Defibrillators are tiny electronic devices whose role is to lead and monitor electrical impulses of the heart and to keep normal heartbeats under control. They are implanted in the chest under the skin.
This device is required in certain people whose heart action is abnormal. Normally, the heart rate varies from 60 to 80 beats per minute. In some patients, due to heart conditions, heart rate can exceed this number or be way below it. This surgery is performed in these people to re-establish normal heart rate and prevent possible complications related to abnormal heart rate.
- As a major improvement over the early devices, the second generation ICDs were designed to detect ventricular arrhythmias (VA) using a probability density parameter based on the concept that, unlike sinus rhythm, ventricular fibrillation did not maintain an isoelectric baseline. This enabled bradycardia pacing ability and they were minimally programmable. This ended the need for separate pacemakers.
- The second generation ICDs could do away with thoracotomy by the introduction of transvenous leads in 1988, which enabled the implantation procedure to be performed in an electrophysiology laboratory rather than open surgery.
- ICDs of today or the fourth generation ICDs have progressively become smaller and more sophisticated. They weigh not more than 80–90 g and have a volume of 30 ml, measuring less than a centimeter in thickness. Newer lithium silver vanadium batteries now last up to 9 years. All modern ICDs carry the ability of overdrive pacing, i.e. ATP, which can often terminate VTs without resorting to shock therapy. In addition, ICDs are also available with biventricular pacing (cardiac resynchronization therapy) to improve symptoms in patients with advanced cardiac failure.
- Indications for ICDs can be broadly categorized as primary prophylaxis and secondary prophylaxis against SCD. Multiple randomized clinical trials have shown ICDs to be clearly superior to antiarrhythmic drugs in patients with a history of life-threatening VT and VF and therefore the indications for secondary prophylaxis are well supported by clinical evidence. However, indications for primary prophylaxis, representing most of the ICD implants, have comparatively less well established evidence, as the measurable quantitative benefit is smaller.
- New ICD and CRT-D devices such as the new Gallant have received the CE Mark recently in February 2020. This new Gallant system, for instance, pairs with the secure myMerlinPulse mobile app to help streamline communication and increase engagement between doctors and their patients. This sort of app-based ICD system which would allow patients to engage more frequently with their healthcare team by providing access to transmission history and device performance and schedule their appointments could be the immediate future of ICDs.
The surgery is performed by well-experienced cardiac surgeons. Patients who have suffered from arrhythmia do not have to worry about the abnormal heart rhythm anymore and to take medications. The defibrillator will control and maintain normal heart rhythm for them.
Defibrillator Implant Surgery- the Very Procedure
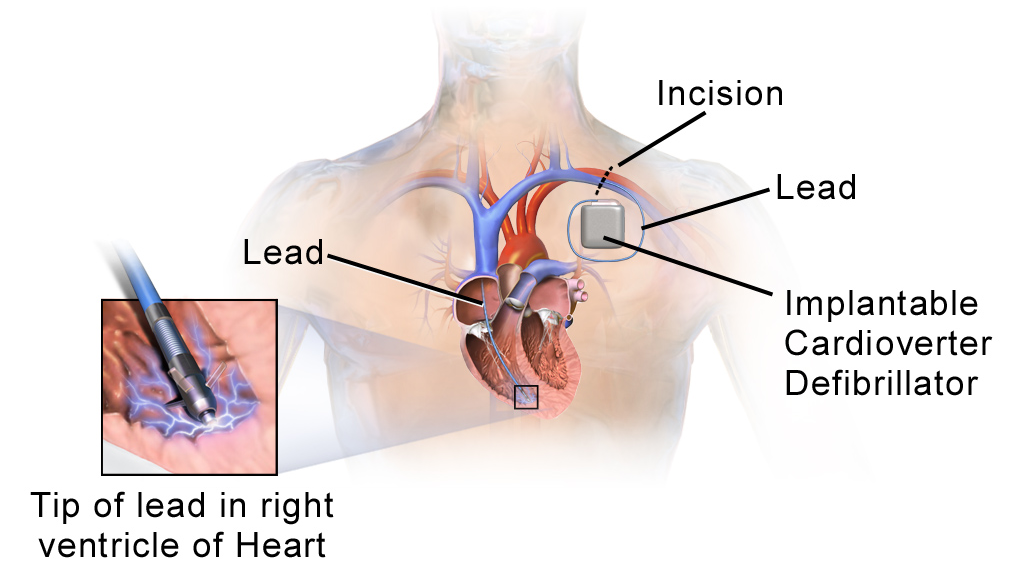
The defibrillator is implanted in the chest under the skin. It can be also implanted above the waistline. The defibrillator contains a generator and wires. Inside the defibrillator, there is a battery that needs to be replaced after a certain period, which varies from patient to patient. The ends of the leads are connected to the heart and the defibrillator. The whole procedure lasts no longer than 2 hours. Still, in complicated cases, it can last up to 5 hours. After the surgery, the functioning of the device is checked.
The patients are hospitalized for a couple of days. After defibrillator implant surgery patients need to refrain from strenuous activities and lifting heavy objects for a certain period. The entire recovery time lasts approximately a few weeks.
The surgery carries certain risks. They include infections and malfunctioning of the very device. Fortunately, there are no severe complications related to defibrillator implant surgery.
After the Surgery
After the surgery has been performed the defibrillator monitors the heart rhythm, and in case of any irregularity, the pulse generator sends specific electrical signals to the heart. These signals restore the normal heart rate. If a heart does not respond to these initial signals the pulse generator gives a shock to the heart, and this finally results in proper heart rate.
The patients need to go for regular check-ups every few months. The device and the condition of its battery are checked as well. This device can function without the need for the battery to be changed for 4 to 8 years. This depends on how many times the defibrillator will be activated.
- medlineplus.gov/pacemakersandimplantabledefibrillators.html
- medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007370.htm
- Photo courtesy of BruceBlaus by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Blausen_0543_ImplantableCardioverterDefibrillator_InsideLeads.png










Your thoughts on this
Loading...