
Amazingly, astonishing facts about the E. coli bacteria have been intriguing numerous scientists around the world. Therefore, they have obtained excessive information about its genetics and many other aspects of its existence, making E. coli one of the most studied living organisms on this planet.
Facts about E. Coli
A few strains of this bacteria have been carefully sequenced and studied, being suggested as candidates for the whole genome sequencing. Basically, it consists of a single circular chromosome which further contains 4,639,221 base pairs and 4,288 protein-coding genes. However, 38% of the protein-coding genes are without any function.
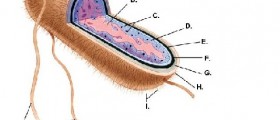
This bacteria colonizes the lower gut of animals, being capable of surviving even when expelled into the natural surroundings. The shape of this bacteria is rod-like, with adhesive fimbriae. Some variants of E. Coli bacteria are known for their power to produce acid by fermenting D-glucose, L-arabinose, and D-mannitol. However, these do not ferment sucrose and lactose.
As for other characteristics of these remarkable organisms, they are beta-galactosidase positive. Yet, they cannot use many different types of less known types of sugar.
E. coli is a bacteria which can be found in the stomach of infants, just a couple of hours after they becomes alive, being the main facultative anaerobe as far as flora of the human colon is concerned. But, when this bacteria contaminates some different tissues, it can trigger infections in the human body, even when the person affected is generally healthy.
Finally, this bacteria can be grown under an optimal temperature of 37 degrees Celsius.
Additional Information about E. Coli
E. Coli has been related to countless occurrences of diarrheal disease, especially frequent in Bangladeshi children. If the host of this bacteria suffers from low immunity or some diseases compromising his/her health, it can cause infections. On the other hand, certain strains of this bacteria have been known to do the same even to people who are generally healthy. Eating undercooked meat or drinking contaminated water are the most common ways of contracting E. coli. Nevertheless, vegetables and other raw, natural products may carry the bacteria too.
Even though E. coli usually affects mucous parts of the body, it may trigger infections in other areas as well. Due to the toxins that this bacteria produces, it triggers diarrhea and numerous other, negative, symptoms. Moreover, E. coli strains which are capable of causing diarrhea, usually affect the small bowel mucosa, where other colonies are not even present.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...