After the recent outbreak of E. coli infections all over Europe, people have become increasingly interested in this bacterium, its effects, symptoms and, of course, ways of treatment.
What is E. coli?
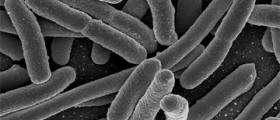
Escherichia coli or E. coli is a type of bacteria that is normally present in the human body for example in the intestines, where it represents a part of the normal bacterial flora. There are many kinds of E. coli and many of them are completely harmless, like those present in the gut. However, other kinds are more serious and capable of causing different kinds of health issues. For example, E. coli is a common cause of bladder infection called cystitis. Other types cause gastrointestinal problems. The most common route of infection is consumption of contaminated foods.
Some strains of E. coli produce toxins that are capable of causing severe health problems. The outbreaks of such infections are usually widely reported on in news, like this latest one in Europe.
The symptoms of E. coli infection vary depending on the location. The strain that made the whole world worried and that was eventually linked to a farm in Surrey, UK, produces symptoms like stomach cramps, vomiting and bloody diarrhea. One particularly serious complication of toxin-producing E. coli is haemolytic uremic syndrome, which may lead to kidney failure.
How is E. coli treated?
There is no universal treatment for all E. coli infections. The medication of choice will depend upon the type, location and severity of the infection.
Cystitis or bladder infection caused by E. coli usually goes away on its own without any particular treatment. The duration is usually somewhere between two and four days. Some doctors prefer prescribing a short course of antibiotics, just to be safe.
Intestinal infections are usually self-limiting too, which means that there is no need to take antibiotics. The treatment is focused on preventing related complications, such as dehydration. Very severe cases of diarrhea caused by E. coli require hospital treatment where rehydration is done by introducing intravenous solutions.
In some cases doctors decide it is better to prescribe a course of antibiotics, especially if the particular strain is identified as capable of causing serious systemic complications.
As for the prevention, the good personal hygiene is crucial, given that the main route of infection is through fecal matter reaching the mouth. This does not just mean washing hands after using the toilet- washing hands is necessary before meals, after using public facilities and transportation, handling shared objects and such.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...