
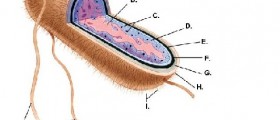
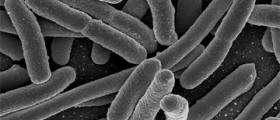
You will know Escherichia coli (E. coli) as a bacteria that can cause severe cramps and diarrhea. The fact, however, is that E. Coli commonly live in the intestines of healthy individuals, and even healthy cattle can carry the E. coli germ. Only certain strains of E. Coli make people sick, but when this happens, symptoms can be quite severe.
Symptoms of an E. coli infection will be worsened by criteria such as age and the presence of another illness. The infection is generally more common during summer. In general, E. coli infections occur as a result of eating undercooked meat, drinking contaminated water or unpasteurized milk or even by working with cattle.
Causes of an E Coli InfectionAs indicated, the most common way that one becomes infected with E. coli is through the consumption of contaminated food. Contamination can be countered through the use of high-temperature cooking. Cooking food thoroughly and over a long period of time can also help to eliminate the bacteria. Undercooked beef is a very common method of transportation of E. coli germs into the human body.
The E. coli bacteria can also move from person to person in a healthcare environment. If one does not wash one's hands correctly and thoroughly, this might increase the risk of spreading the infection. Those who are infected with certain strains of E. coli bacteria, such as E. coli 0157:H7, are highly contagious. Children should not be admitted to day care centers until the infection is conclusively proven to have been eliminated — because they are contagious up until that point. Once the bacteria have been proven to no longer be present in the person's stool by way of a lab test, they are no longer contagious.
What does this mean, exactly? You should know that:
Frequent handwashing is advised, both on the part of the infected person and anyone who touches the infected person. People infected with E. Coli should not cook or prepare food for other people. Watch out for oral and fecal transmission — wear gloves if you are caring for a child or elderly person infected with E. Coli, consider wearing a surgical mask, and do not drink from the same glass of water they have. SymptomsSymptoms of E. coli infection include the severe and sudden onset of stomach cramps, as well as diarrhea. Diarrhea can lead to serious dehydration and fluid loss. As a result, you might feel tired and sick. Fever, nausea and vomiting are all potential symptoms of an E. coli infection. Complications of the infection include a disorder known as hemolytic uremic syndrome. This condition can lead to hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia and renal failure. However, this is more common in children than in adults.
TreatmentSpecialized E. coli infection treatment can be quite non-specific. The main way to combat the infection is to drink plenty of water. One should also take care to notice any complications that might occur. Severe dehydration might require an intravenous drip to be administered in a hospital environment.
Prevention is in fact more important than treatment, so be sure to carefully wash your hands before coming into contact with food. Cook meats thoroughly, avoid cross-contamination of cooked and uncooked meats, defrost meats correctly and be sure to keep meat and poultry separate from other foods. Try to avoid the consumption of raw milk.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...