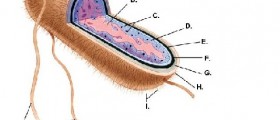
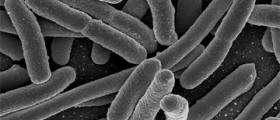
Escherichia coli, also known as E. coli, are a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium that typically inhabits the lower intestines of humans and other warm-blooded animals. Escherichia coli are normally harmless and their population is managed and kept in balance by other beneficial bacteria found in the human body. Harmless strains of Escherichia coli can even be beneficial, by producing vitamin K2 and preventing overgrowth of pathogenic bacteria inside of the intestines. However, there are a couple of particularly dangerous strains of Escherichia coli, and some of them are known to cause severe food poisoning in humans, and the infection with these strains may often have fatal consequences. One of the most dangerous strains of Escherichia coli is known as E. coli 0157:H7
The symptoms of E. coli 0157:H7 infection
In most cases, first symptoms of infection with this dangerous strain of Escherichia coli will become observable within 3 to 5 days following the contamination. Normally, people are becoming infected by swallowing the bacteria through food, contaminated water, or by touching contaminated surfaces and then touching the mouth.
In the early stages, the infection manifests as a simple abdominal upset. A patient may experience stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and later may have diarrhea that is often bloody. As any other kind of bacterial infection, this one may also be accompanied by mild fever, usually about 100 to 101F. Normally, the infection will resolve in a couple of days, if treated timely and properly with antibiotics. However, younger children, elderly population and people with compromised immune system or other underlying diseases, may experience more troubles. These patients will often need hospital care and more aggressive treatment to prevent any of the associated complications. The most severe complication of this bacterial infection is death.
How to prevent E. coli 0157:H7 infection
In most cases, people are becoming infected when they eat raw or undercooked ground beef or drink raw milk. The food is contaminated in the contact with animal feces containing bacteria. Less commonly, the bacteria are spread from one person to another, during a direct physical contact.
The only way to prevent this infection is to cook meats thoroughly to a temperature of at least 160 F. People should also avoid any kind of unpasteurized dairy products, unpasteurized juices and drinking raw milk. In some cases, people are becoming affected when they swallow water from pools, lakes, ponds, or other recreational waters. Therefore, it is necessary to avoid drinking from these sources. People should wash their hands on a regular basis and always after contact with animals.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...