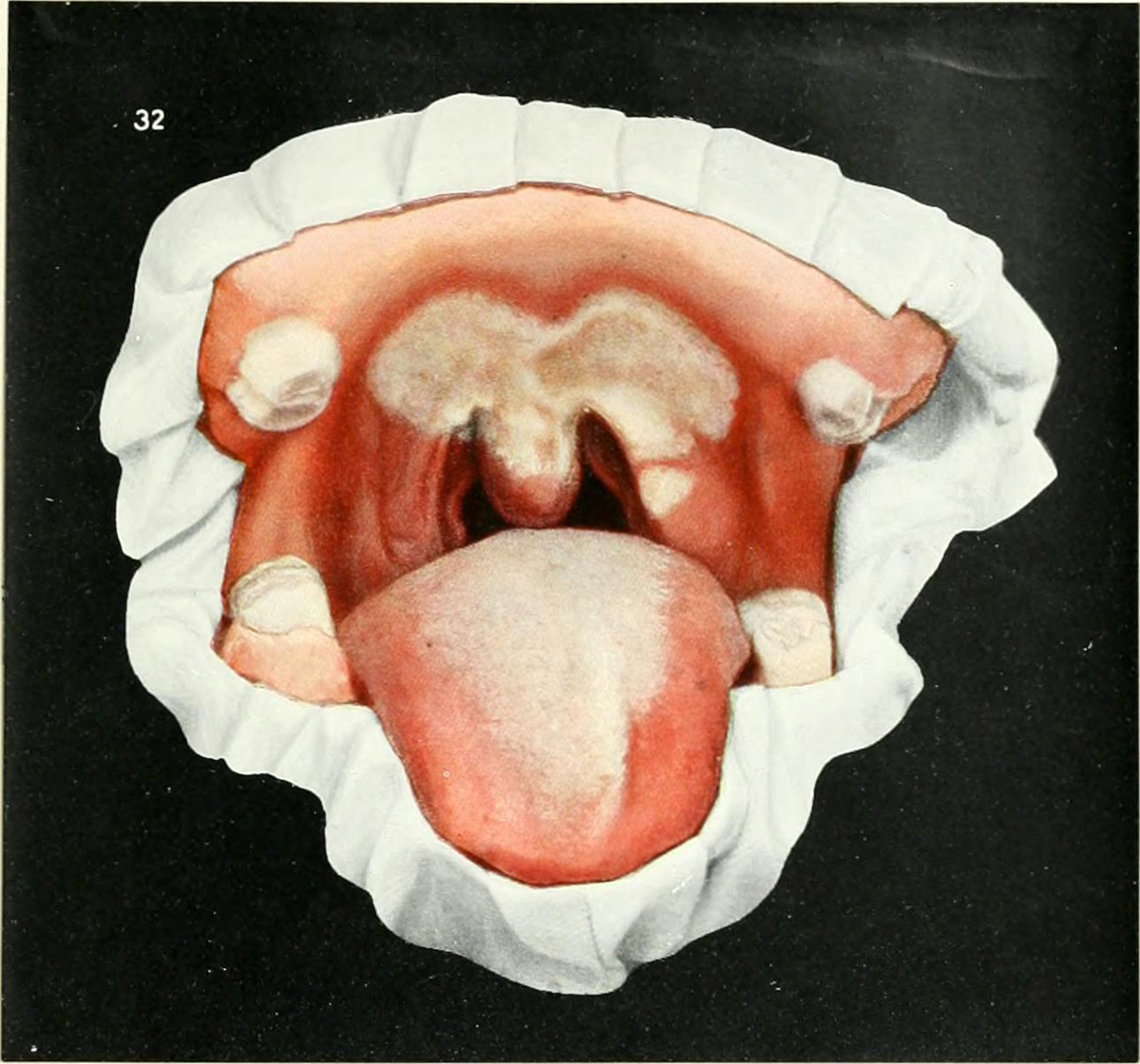
Tooth damage often occurs as a result of the usage of drugs, both licit and illicit. Drugs that can cause tooth damage include antihistamines, Aspirin, asthma medications and syrups, cocaine, crack, ecstasy, heroin and methamphetamines. Treatment should focus on prevention rather than the cure, as dental restorations can be time consuming and expensive.
Drugs
Antihistamines can lead to dry mouth and gum problems. Aspirin might lead to direct tooth damage, so try to only use Aspirin as directed. Try to swallow the tablet whole, rather than chewing. Asthma medications are acidic and might lead to a dissolution of tooth enamel if prolonged usage occurs. Drugs that are used in the process of chemotherapy might lead to dry mouth and an increased risk of exposure to gum problems. Immunosuppressive drugs and oral contraceptives can also cause similar kinds of problems. Medicated syrups containing high amounts of sugar might also increase the risk of tooth decay. Certain kinds of drugs might lead to a thickening of the gum tissue, a condition known as gingival hyperplasia. Drugs such as this include epilepsy medications, cyclosporin, blood pressure medications and calcium channel blockers.
Smoking and drinking alcohol also lead to dry mouth and tooth damage. Alcohol is acidic, while smoking can lead to gum problems. Other illegal drugs can also lead to significant damage of the teeth. Amongst these drugs are cannabis, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, and methamphetamines. Cannabis leads to dry mouth and gum problems, while cocaine is acidic in its nature and can erode tooth enamel. Ecstasy leads to dry mouth, as do methamphetamines. Heroin and methamphetamine usage can lead to tooth decay - heroin can lead to cravings, while ‘meth mouth’ is a common result of the usage of methamphetamines.
Treatment
Treatment will of course depend on the drug and the resultant effects. A dentist might recommend a reduction in dosage, if medication use is the cause of dental health problems. A switch of medication might also be advised. Professional and at-home protection treatments can also be used. Topical fluoride applications can reduce the risk of decay. Decayed teeth might require fillings, or even restorative work. Extraction or removal might also be necessary in some severe cases. If gingival hyperplasia is the cause, the dentist might advise the trimming of the affected gum tissue. In cosmetic terms, veneers might also be used in some cases, to improve the overall outward appearance of your teeth, mouth and smile.



_f_280x120.jpg)











Your thoughts on this
Loading...