The human body has five senses:
1. Seeing
2. Smelling
3. Tasting
4. Touching
5. Hearing
Each of these senses has its main organs through which the senses are manifested. Thus, the main organ for the sense of seeing is the eye, while the main organ for the sense of smell is the nose. Furthermore, the organ for tasting is the tongue and the main organ for the sense of touching is the skin. The sense of hearing has its main organ as well, and that is the ear.
The ear is part of the auditory system in humans and its structure is very complex. The main role of the ear is to receive sound waves and transmit the signals to the brain. Another function of the ear is to keep the balance of the body.Different Parts of the Human Ear
The human ear is made of three major parts and these parts are further comprised of other parts. The three major parts of the ear are the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear.
The outer ear collects the sound waves that travel from the outer ear to the middle ear. In the middle ear, the sound waves are transformed into compressional waves, which then travel to the inner ear. In the inner ear, the compressional waves are transformed into electric impulses that the brain perceives.
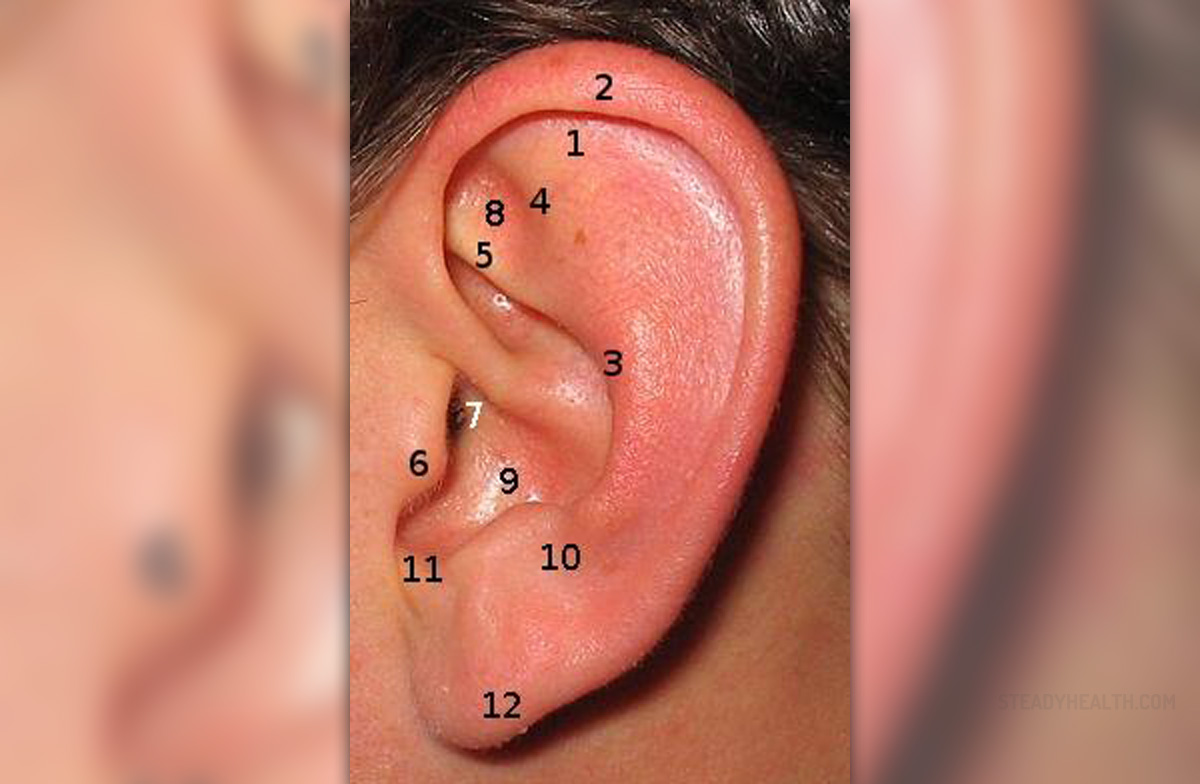
Outer Ear
The part of the era that we can see is the external or outer ear. It has the role to protect the eardrum and to collect sound waves. It is comprised of two parts, the ear flap, which is called pinna, and the ear canal, which is called the meatus.
Ear flap serves for collecting the sounds, while the ear canal, which is long 2 cm by the way, serves as a canal for the sound waves that travel to the middle ear. In this part of the ear are sweat glands that produce earwax.
Middle Ear
The middle ear is filled with air. It is made of four parts: eardrum, hammer or malleus, anvil or incus, andstirrup or stapes.
The role of the eardrum or tympanic membrane is to part the outer and the middle ear and to vibrate when it receives sound waves transforming them into mechanical energy. Hammer, anvil, and stirrup are three tiny bones that are located near the eardrum and they vibrate and pass the waves next to the inner ear.
Inner Ear
The inner ear is made of the cochlea, semicircular canals, and auditory nerve.
Cochlea is also called a spiral tube that has a membrane full of nerve cells that convert the waves into electric impulses. Semicircular canals help in maintaining balance, while the auditory nerve passes the electrical impulses to the brain.
- The vestibular apparatus of the inner ear is responsible for the static and dynamic equilibrium of the human body.
- The analysis revealed that the human ear is a perfect design because it is an uncoupled structure. It is not only a perfect design but also a low-cost design. The materials that are used to build the ear atom-by-atom are chiefly carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, calcium, and nitrogen. The material cost is very negligible, which amounts to only a few of dollars.
- The ear is not designed to pick up bodily sounds, such as the constant rushing sound of blood through the blood vessels near the ear. Sound waves are conducted through the bones of the skull, but the ossicles do not respond to them with the same sensitivity as they respond to tympanic movements.
- The ear is equipped with a truly impressive selectivity. It filters out low frequencies, amplifies mid frequencies, and enhances spatial perception through direction-sensitive filtration of high frequencies. In their own way, pinna, concha, and external ear canal perform sound wave amplification. When sound waves hit the head at 45° angle, the pinna amplifies 4 kHz frequencies to a peak of 3dB. The concha can amplify 4–5 kHz wave to a maximum gain of 10 dB. The ear canal also provides a peak gain of 10 dB at 2.5 kHz. All external ear components together amplify frequencies in the range of 2 kHz to 5 kHz with the maximal gain of 20 dB at 2.5 Hz.
- Certain physiological features embedded in the ear enable the sense of the body’s equilibrium. Saccule perceives the orientation of the head when the body is static. Utricle perceives linear acceleration when the body is in straight-line motion, such as when riding a car or elevator. While macula sacculi are positioned vertically on the saccule walls, macula utriculi are laid horizontally on the base of the utricle.
- Development of the ear begins at the third week of gestation and positions itself in full form, level with the eyes, at around the 32nd week of gestation. It can grow into a bigger size (from childhood to an adult), self-repair, and self-heal. It is built inside the mother’s womb using nano-scale mechanisms: self-assembly, massive parallelism, and hierarchy.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...