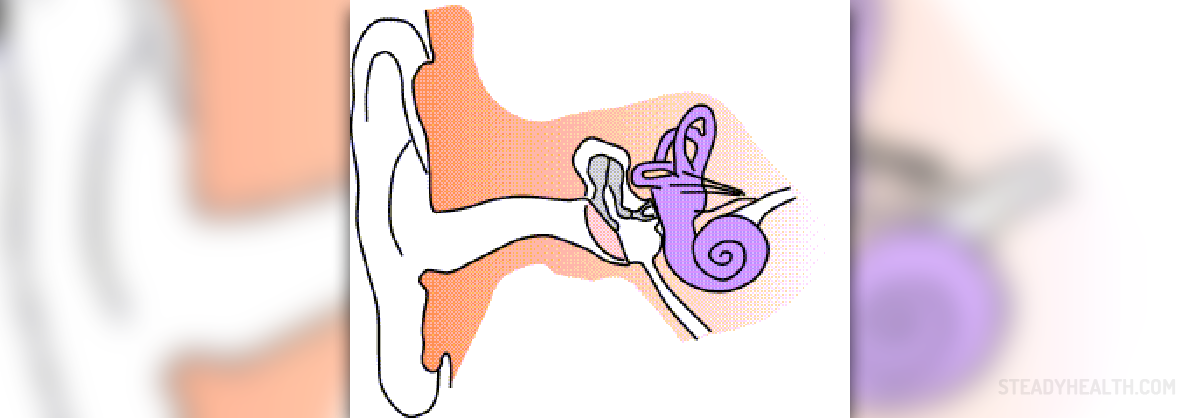
Ear Anatomy and Ear FunctionsThe ears consist of five components and each component performs different functions that are important for process of hearing. The ear is composed of:Outer earMiddle earInner earAcoustic nerveCentral Auditory Processing CentersOuter Ear
The outer ear is composed out of the pinna and external auditory meatus. The pinna or the auricle is the outer and visible part of the ear that is attached to each side of the head. The pinna collects the sounds and transmits them into the ear canal. This part of the outer ear consists of the cartilage and soft tissue.
The external auditory meatus or an ear canal is approximately ¼ inch in diameter. It runs from the pinna to the ear drum or tymapanic membrane. Its function is to recognize the pathway of the sound. In this part of the outer ear modified sweat glands that produce ear wax are located.
Middle Ear
The middle ear extends from the ear canal. It is composed out of the ossicles, three tiny bones that link the eardrum to the inner ear. Sounds that are passed through the pinna reach the eardrum. When exposed to the sound waves, the eardrum vibrates and causes the ossicles to move. This way the sound waves become the mechanical vibration.
The ossicles are malleus, incus and stapes. The malleus or the hammer is positioned between the eardrum and the incus or the anvil which is connected to the stapes or stirrup. The three bones create the ossicular chain and its main function is to amplify the sound. The Eustachian tube also known as the ear tube extends from the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. It acts by providing ventilation and access to the outer air as well as balancing the air pressure on each side of the eardrum.
Inner Ear
The inner ear is made up of the sensory organs that aid in hearing and sustaining balance. The cochlea is the part of the inner ear that is responsible for hearing while the semicular canals that consist of the urticle and the saccule play a role in balancing the body. The cochlea is snail-shaped bony structure that is filled with endolumph and perilymph fluid. Inside of the cochlea is Organ of Corty which represents the sensory receptors necessary for hearing.
Acoustic Nerve
The acoustic nerve carries impulses from the cochlea to the cochlear nucleus in the middle brain area and toward the auditory cortex of the brain. The nerve fibers in the cochlear nucleus transmit information received from the ears to the both hemispheres of the brain.
Central Auditory Processing CentersThe central auditory processing centers are involved in different function of the ear. These functions include: the localization and lateralization of the sound waves, distinguishing between various sounds, temporal resolution, masking, integration and ordering and reducing the auditory performance in presence of competing acoustic signals or degraded acoustic signal.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...