
Hearing loss or hearing impairment is a condition in which the person’s ability to detect certain frequencies of sound is completely or partially impaired. This condition is also known under the name deafness, and the term hearing impaired is commonly rejected and substituted with terms deaf and hard-of-hearing. Hearing loss is therefore diagnosed whenever a person has diminished sensitivity to the sounds that are normally heard by other human beings. Normal hearing thresholds are different among different species. Certain animals, for example, are able to hear sounds that are undetectable to human ear. There are many different types of hearing loss and all of them are evaluated, in the terms of their severity, according to the increase in volume that must be made (and above the normal level) before the individual succeeds to detect the sound. Here is a quick review of different types of hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss
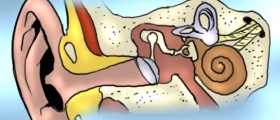
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a problem in conducting the sound waves. The problem exists anywhere along the route through which the sound waves need to travel before they reach the middle ear: outer ear, eardrum, middle ear or the very inner ear. Sometimes, this obstruction occurs alone and it is the only cause of hearing loss. In other cases, it exists together with sensorineural hearing loss, which is the other main type of deafness. The most common sources of conductive hearing loss are ear infections and accumulation of ear wax. However, the problems with hearing may also occur when the foreign body enters the ear canal, or as a result of some other health problems such as tumor of the ear canal, congenital atresia or because of the formation of new bone on the surface of the bone. Tympanic membrane perforation can also cause hearing loss.
Sensorineural hearing loss
This type of hearing loss is caused by the vestibulocochlear nerve, problems in the inner ear, or processing centers in the brain. People affected by this type of hearing loss can be only mildly impaired or may be totally deaf. The root of the problem are defects in the hair cells of the organ Corti in the cochlea. The organ of Corti is the organ in the inner ear that contains sensory hairs. When the hair cells are damaged, they do not regenerate, and the person loses the sensitivity to sounds. Some other, rare types of sensorineural hearing losses include problems with eighth cranial nerve or defects in the auditory portions of the brain. Problems with brain are the rarest sorts of hearing loss.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...