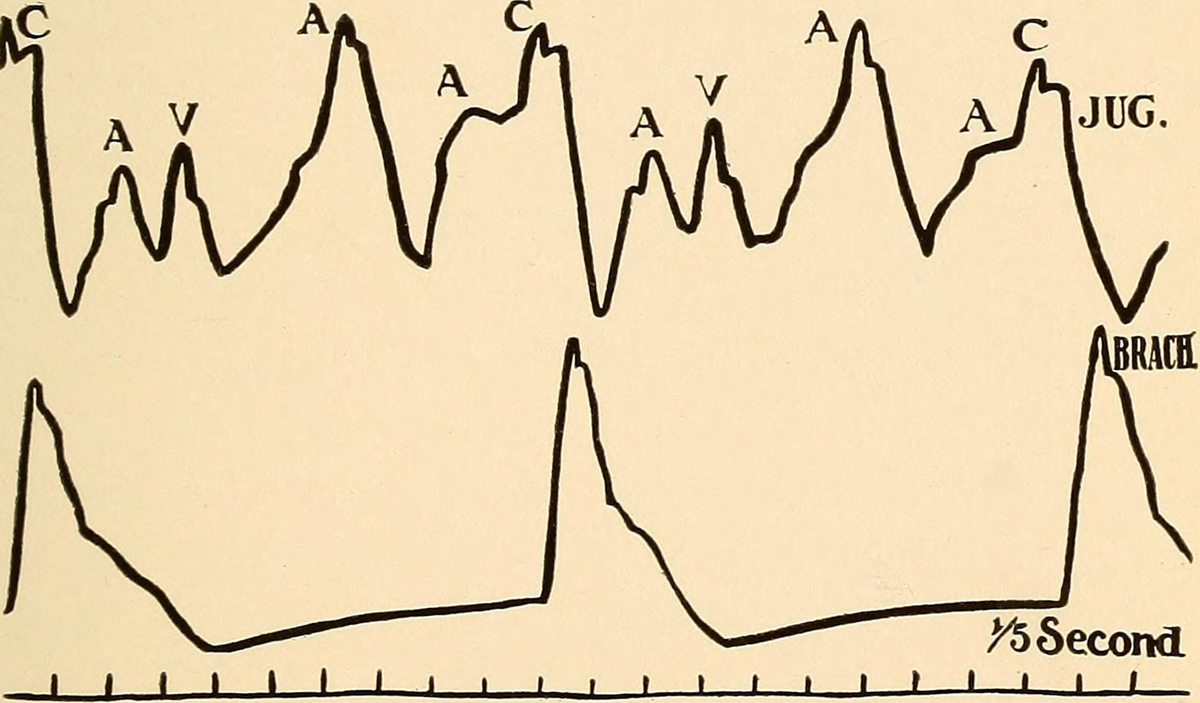
Irregular Heartbeat
Irregular heartbeat is medically known as arrhythmia. Normal heart rate is between 60 and 75 beats per minute. In arrhythmia heartbeats either slower or faster than optimal. If hearts beats slower, this condition is called bradicardia and if it is accelerated the condition is called tachycardia. Even some other abnormalities in heart rhythm are classified into arrhythmia.
Symptoms of Irregular Heartbeat
Symptoms of irregular heartbeat can be rather indistinguishable. This condition, for example, may be completely asymptomatic. In this case it is most frequently found during routine physical examination. Even patients suffering from severe arrhythmia may have no symptoms or they complain about not so serious symptoms. On the other hand, there are patients who suffer from severe symptoms of the disease.
Patients who do have symptoms and signs of the disease report intermittent chest pain or angina. They may also complain about rapid heartbeat. In extreme forms of arrhythmia patients may even faint. Additional symptoms include breathing difficulties, particularly during strenuous physical activity and a feeling of fluttering and flapping in the chest. And finally, confusion and problems with concentration may occur as well.
Causes of Irregular Heartbeat
Contraction of the heart is regulated by electrical signals that are formed in the heart and signals which come from the brain. Any cause that leads to interruption or excessive production of electrical signals may lead to arrhythmia.
Coronary heart disease may be one of the causes of irregular heartbeat. Furthermore, external triggers and stimulants such as smoking, alcohol consumption, increased intake of coffee and drug abuse may stimulate the heart and lead to arrhythmia. Increased intake of certain electrolytes such as sodium and potassium is another cause of arrhythmia. The heart may skip a beat if some cough and cold medications are taken because they may contain certain stimulants. Postoperative period after heart surgery may be accompanied by irregular heartbeats. Hypertension and hyperthyroidism may also induce arrhythmia. And finally, scarring of the heart, which typically occurs after heart attack, interferes in normal production of electrical signals and this consequently results in arrhythmia.
Diagnosis of Irregular Heartbeat
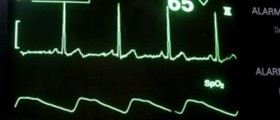
There are several standard tests which can help in diagnosis of irregular heartbeat. Electrocardiogram (EKG) and holter are excellent methods in diagnosing arrhythmia. Additional tests such as blood count, echocardiography and chest X-ray are helpful in identification of the underlying cause of arrhythmia.
Treatment for Irregular Heartbeat
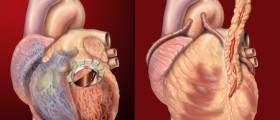
People suffering from irregular heartbeat are usually prescribed antiarrythmic medications. In some cases symptoms of irregular heartbeat may withdraw once the underlying disease has been brought under control. Bradicardia is treated by implantation of pacemaker. And defibrillators are implanted in patients suffering from life-threatening arrhythmias.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...