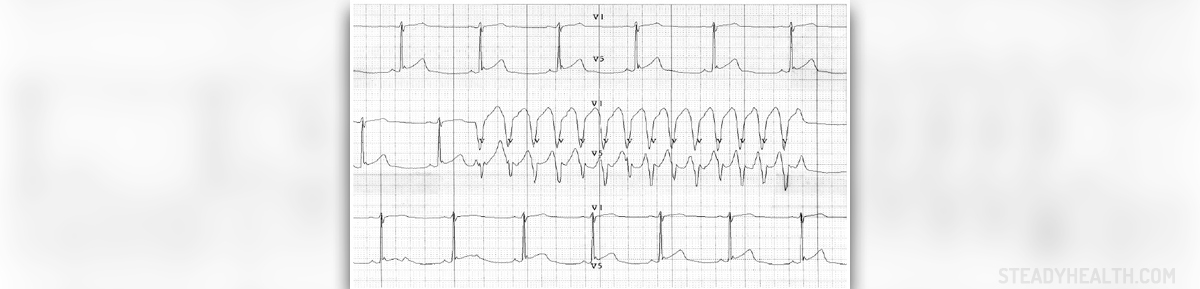
The healthy heart of an adult person beats 60 to 100 times per minute, when the person is resting. Any beat, higher than 100 at rest is considered tachycardia. This condition appears when the heart creates fast electrical signals, which are then sent through the heart, making it beats faster.
Tachycardia may be just the symptom of another heart condition or problem with the thyroid gland. In that case, treatment for the cause is helping with the existing tachycardia.
Sometimes, there are no visible symptoms or complications of tachycardia, but untreated condition may lead to heart attack, angina or ischemic heartdisease. The therapy is working to slow the tempo of the heart, prevent the condition and minimize eventualcomplications.
Vagal maneuvers are simple actions, something you yourself can do when your heart rate speeds. Try to gag, cough, immerse your head in icy water or hold your breath and bear down. Pressing your eyelids may slow your heart too.
Medication is necessary when vagal maneuvers don’t slow down the heart. The doctor could prescribe some anti-arrhythmic tablets, flecainide (Tambocor) or propafenone (Rythmol), or if you are already in the hospital it is more likely to have an anti-arrhythmic injection. In the ER (emergency room), when vagal maneuvers or medication are not efficient, the doctor could perform cardioversion. An electric shock is send to your heart and that brings the rhythm to normal.
Sometimes it could be possible to prevent future episodes of tachycardia, using medications, surgery, catheters or defibrillator. Medications in use for this purpose are anti-arrhythmic drugs, which may be combined with diltiazem (Cardizem), verapamil (Calan), propranolol (Inderal) and esmolol (Brevibloc). Tachycardia episodes might put you at risk to develop a blood clot, which could lead to and stroke and heart attack. To avoid that kind of complication, your doctor may give you blood-thinning medications.
Some types of tachycardia are treated by catheters inserted in cardial (of the heart) blood vessels. Electrodes on the catheter produce the heat and destroy the abnormal pathways in the heart, responsible for the tachycardia. Life threatening tachycardia is often resolved by implantation of a defibrillator. The device is constantly checking your heart and when the heart starts to beat faster than it should be it releases an electric pulse and regulates heartbeats.
Surgery might be the final option to resolve tachycardia, if all of the procedures above happens to fail. The surgeon will make scars on the heart tissue, in order to prevent the conduction of the abnormal electric pulses.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...