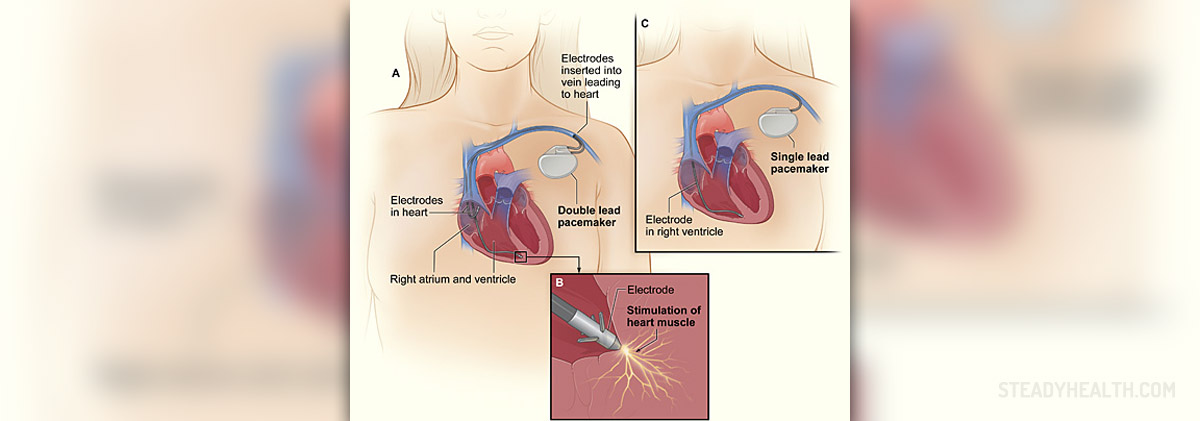
A pacemaker is a certain type of device which is intended to send electrical pulses to the heart muscles so that a normal heart rate can be maintained. A pacemaker is also very efficient in stimulating the ventricles. For those who do not know, ventricles are the lower chambers of the heart. In some cases, pacemaker may be used for the treatment of several different types of medical conditions such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congestive heart failure and fainting spells. There are different types of pacemakers which are used for different types of heart conditions and can be characterized by different minimum heart rates to which they need to be set. Once the heart rates below the certain minimum rate, the pacemaker generates the artificial impulse, contracts the heart muscles and thus creates a heartbeat.
Electrical System of the Heart
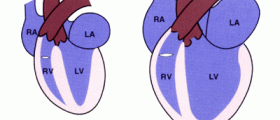
The electrical system of the heart is actually the power source which makes the alternate contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles, which work together so that the blood could be pumped through the heart. The sinoatrial node is located in the right atrium of the heart and it is the source of all electrical impulses, from which they all spread out through the walls of the atria so that they can contract properly. The electrical impulses then travel through the AV node which is located between the ventricles and the atria. This node is in charge of slowing the electrical signals before they get to the ventricles. The next stage of the travels of the electrical impulses is the His-Purkinje network which consists of a pathway of fibers especially efficient in conducting electricity. From here the impulses travel further to the muscular wall of the ventricles. A pacemaker is required in all situations in which the electrical pathway does not function the way it is supposed to and when certain changes in the heart rhythm and rate occur.
Pacemaker Procedure and its Risks
Pacemaker implant is an invasive type of surgical procedure, so like any other, it is involved in certain risks, but in most cases it is a completely safe procedure due to certain precautions taken so that the risks can be reduced. Persons who are about to undergo a pacemaker implant usually need to stop taking warfarin and Aspirin a few days before the actual procedure. Certain other types of medications may also need to be stopped prior to the surgery. These matters are commonly discussed with the doctor. Those who suffer from diabetes may need to readjust the dosage of insulin and diabetes medications. The patient is not allowed to eat or ingest any fluids before going to bed prior to the surgery. All nail polish and makeup need to be removed, and the person is supposed to wear a hospital gown during the procedure. All valuables, watches and jewelry must not be worn during the procedure. The procedure is commonly performed in the pacemaker lab. The nurse first starts an intravenous line, which is there to provide the fluids and the medications during the procedure. This includes the antibiotics. The chest needs to be shaved and cleansed with a special soap. The procedure does not involve putting the patient to sleep, but certain medications are used to make him or her feel drowsy. During the procedure, the patient is constantly monitored. The monitors used during the procedure include fluoroscopy, which is a big X-ray machine, oximeter monitor which check the level of oxygen in the blood, blood pressure monitor, electrocardiogram which checks the electrical impulses in the heart and the defibrillator which regulates the heart rate. As already explained, a pacemaker implant may be associated with certain risks, like any other surgical procedure. One of the possible risks is a perforation in the muscle layer of the heart which may trigger an unwanted fluid buildup around the heart. Another possible risk during a pacemaker implant is an air leak around the lungs. One may also experience certain problems with the pacing leads, which usually occur when one of the leads moves out of its normal position. The most common types of risks which may be associated with the pacemaker implant are various sorts of infections.
After the Procedure
Once the procedure is done, the person needs to stay at the hospital for two days. Once the doctors determine that the implantation was successful, the patient is free to go home. During the hospital stay, the patient is constantly monitored by a device called the telemetry monitor. Another type of monitor which is attached to the patient by sticky electrode patches is called the holter monitor. There are certain tests which need to be performed following the procedure. Those tests include an X-ray scan of the chest. The patient may feel slight discomfort for 2-3 days after the procedure.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...