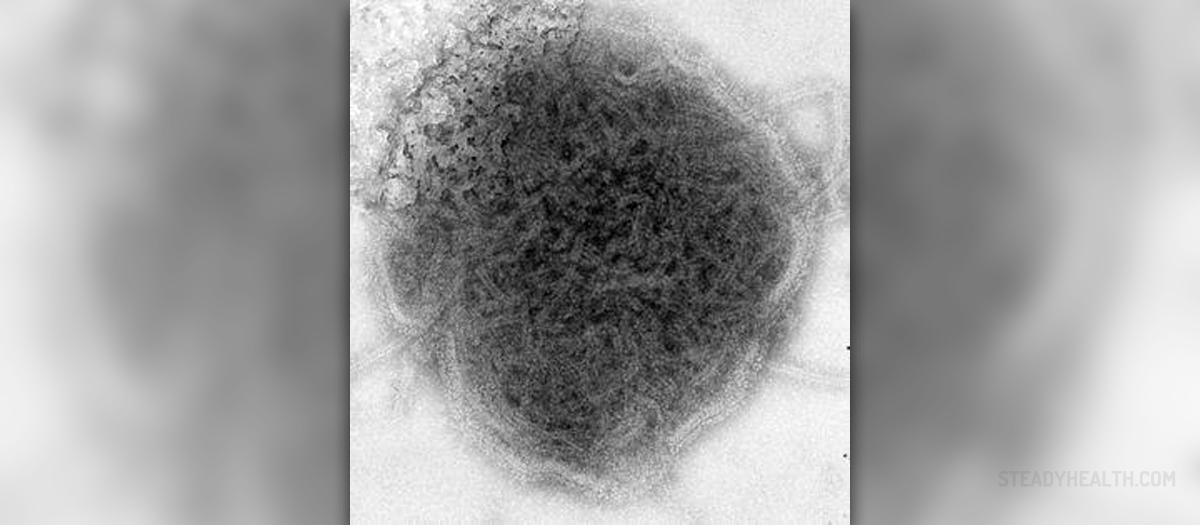
Mumps is a contagious viral disease predominantly affecting the salivary glands. The virus responsible for the infection is easily transmitted from an infected person to other people by respiratory droplets (while coughing or sneezing) or by direct contact with objects contaminated with infected saliva.
In majority of cases mumps affects children between the age of 2 and 12, those who have not been vaccinated against the disease. After being exposed to the virus, the symptoms of the disease develop after approximately 12-24 days.
It is essential to mention that apart from affecting the salivary glands, mumps may also cause inflammation of other organs/organ systems in the body such as the central nervous system, pancreas and testicles. Some children may also lose their hearing, which is considered quite a serious complication of the disease.Mumps Clinical Characteristics
The infection can be mild and only cause sleepiness, muscles ache, headache and noticeable loss of appetite. Fever is always present. The inflammation of the salivary glands, predominantly the parotid gland, leads to an increase in the size of the gland which gives the person's face a puffy appearance. The infection is not so severe but it may get worse and cause additional health problems.
Hearing Loss After Mumps
As for potential complications, it is essential to mention that it may not be immediately apparent that a child has developed hearing loss. This complications may even be more complex to be noticed in babies. This health issues, on the other hand, can be easily detected in older children.
Hearing loss associated with mumps may affect one or both ears. It is estimated that this complication occurs in approximately 1 out of 20,000 cases. The health issues develops suddenly. Most patients, fortunately, experience hearing loss on just one ear. Finally, in around 100 children who have suffered from mumps hearing loss will be permanent.
Because hearing loss generally affects only one ear, it may be difficult to detect the problem. This is the reason why such children are due to have their hearing tested after certain period of time (usually after 6 to 12 months).
What if there is Hearing Loss?
Even if a child has developed hearing loss, he/she can still be treated. One option includes hearing aids. Another one are cochlear implants. It is essential to learn and adopt new communication skills, particularly if there is complete hearing loss. These include sign language, lip-reading and cued speech.
The infection and potential complications can be prevented by the MMR vaccine, a vaccine efficient against three illnesses, measles, mumps and rubella.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...