
Noise-induced hearing loss is a medical condition that develops due to exposure to loud noise and sounds originating from our environment. This problem predominantly affects people who are prone to listening to loud music, musician who perform live, DJs as well as some people whose occupation is connected to chronic exposure to loud noise.
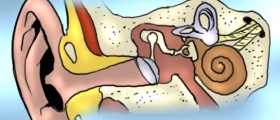
Loud sounds, particularly if they are repeated or last for a long period of time, are responsibly for damage to sensitive structures in the inner ear (hair cells as well as small sensory cells) and subsequently lead to noise-induced hearing loss.
Sounds Capable of Causing Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Hearing loss of this kind can be caused by a simple event such as an explosion or develops as a consequence of continuous exposure to loud sounds for prolonged period of time. One example of such prolonged exposure is noise generated and released in a woodworking shop.
Scientists have confirmed that prolonged or repeated exposure to sounds at or above 85 decibels eventually leads to hearing loss. Damage is always more severe if one is exposed to sounds of more decibels.
The Effects of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Loud noise is responsible for the damage to specific cells inside the inner ear or the auditory nerve itself. Impulse sound of great intensity may cause immediate and permanent hearing loss and it occurs together with additional symptoms such as tinnitus. Prolonged exposure to noise is accompanied by severe damage to hair cells of the inner ear. The previously mentioned damage can be successfully prevented by using hearing protectors like earplugs or earmuffs.
Symptoms of hearing loss tend to increase gradually. Initially, one may be able to recognize sounds while later the sounds become distorted or muffled. This makes an affected individuals practically unable to understand speech. It can be that the person is not aware of the damage to the auditory system. In such case hearing loss can be detected and confirmed with a simple hearing test.
Who is at Risk for Noise-Induced Hearing Loss?
The condition affects people of all ages. In the US the vast majority of patients affected by this type of hearing loss are between the age of 20 and 69.
The risk is increased if there is prolonged exposure to loud sounds, noise at work and in leisure activities. Furthermore, even recreational activities such as target shooting, hunting, snowmobile riding, woodworking etc. may be associated with noise-induce hearing loss. Prevention
Prevention of noise-induced hearing loss is possible. All a person needs to do is to abstain from exposure to sounds that are greater than 85 decibels. If this is not possible, he/she is due to use protective earplugs and other hearing protective devices. People who indulge in leisure activities that include exposure to loud sounds should think twice before they opt for a particular activity, especially if they are already suffering from certain degree of hearing loss.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...