Introduction
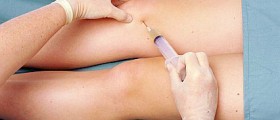
Hip arthroscopy is usually performed with laparoscope small surgical instrument with camera and light that allow the surgeon to see inside of hip joint. The surgical procedure is performed through one or several small incisions. This surgical procedure is considered to be less evasive that other ones.
There are several benefits of Hip arthroscopy surgery and some of them are accelerated rehab course, early and speedy rehab, smaller incisions and easier outpatient procedure.
Condition That Can be Treated with Hip Arthroscopy
There are several common conditions that can be successfully treated with hip arthroscopy and here is a list for some of them.
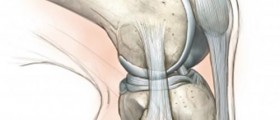
Cartilage damage
In cases of focal cartilage damage, which means that arthritis is not widely spread to the joint, hip arthroscopy can be performed successfully. Usual case is when patient have piece of cartilage broken away from bone surface, and usually broken piece is removed.
Snapping Hip Syndrome
Snapping hip syndrome occurs in cases when something is snapped within hip joint. Hip arthroscopy can help in those cases to relieve the snapping, and it can be used in cases of psoas tendon too get released.
Labral Tear
Cuff of thick tissue in the hip joint is called labrum, and it helps to support the hip joint. In cases when labral tear in the hip occurs piece of tissue becomes pinched in the joint. Hip arthroscopy can successfully relive the problems in those cases.
Early Arthritis
In cases of early arthritis, hip arthroscopy procedure is somehow controversial; meaning there is no evidence that procedure will help patients with those symptoms. Only the cases of arthritis patients who have pinching in the hip joint can be sure that hip arthroscopy will remove the bone spurs responsible for this pinching. Of course success of this surgical procedure depends of early stage of arthritis in patient.
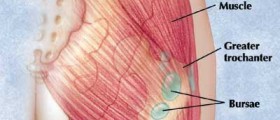
Possible Complications from Hip Arthroscopy
Usual causes for concern in cases of hip arthroscopy surgeries are blood vessel and nerves in the hip joint. Although nerve injury is very uncommon, there is a possibility of damage of the central sciatic nerve, pudendal nerve or lateral femoral cutaneous nerve. Nerve injuries can cause pain and other complications.
Other possible complications of hip arthroscopy may be continued pain after surgery infection in the places of incisions or inside a hip joint or potential injuries of normal structures.
Although all of these complications are very rare, doctors must warn patient of them in advance. But the truth is that with many benefits of hip arthroscopy, possible post operative risks are very small.
Hip arthroscopy is a relatively safe procedure and most complications are preventable. Any surgeon wishing to embark on a career in hip preservation surgery should receive appropriate education in the form of a fellowship, a cadaver-training programme and ideally a mentor who is available for the first few procedures. A precise surgical technique, appropriate instrumentation and adherence to advice from experienced colleagues are all essential factors for a successful outcome. Common tips for preventing complications include:
- Continuous traction should not exceed two hours. Intermittent traction should be used if needed.
- The traction force should be limited to 22.7 kg (50 lbs).
- The perineal post and foot plate/boot must be heavily padded with soft material.
- The extremity should be positioned correctly in slight abduction and flexion.
- Distraction should not be less than 10 mm.
- The joint should then be distended with 20 ml of normal saline and the labral silhouette seen for safe access into the joint.
- Inflow fluid pressure should be low (up to 50 mmHg).
- Post-operative range of movement exercises should be initiated as soon as pain allows.
- Pharmacological prophylaxis should be administered on an individualised basis to prevent infection heterotopic ossification and DVT.
- Minimise capsular dissection in patients with demonstrable capsular laxity.
- A centre-edge angle less than 20° is a contraindication for acetabular rim trimming.
- The osseous deformity should be exposed adequately before resection.



-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)






Your thoughts on this
Loading...