Definition
Gynecomastia is flourishing of breast tissue in men. The name comes from the Greek language and means "a woman's breasts." One of the three men under the age of 40 have some stage of gynecomastia and above age of 50 almost half of men have this disorder.
Causes
An increase in male breast can be a normal physiological phenomenon in certain life-period or a consequence of the disease.
Normal, physiological gynecomastia
Neonatal gynecomastia occurs after birth due to crossing mother's hormone estrogen in the child’s blood during childbirth. The increase is usually reduced for a few weeks, rarely lasts longer.
Construction of the breast tissue in men usually starts at puberty (adolescent gynecomastia) when excess female hormone estrogen infringes the hormonal balance. Most teenagers have increased breast only temporarily, rarely after age of 20. An increase in is often asymmetric breasts are increased unevenly, and sometimes only one breast is increased. Also they can be sensitive to the touch.
Gynecomastia of aging also occurs in healthy men as normal phenomenon. It appears due to the increased conversion of male sex hormones into female. Additional causes of gynecomastia can be medications and liver function disorders.
Gynecomastia caused by diseases
Pathological gynecomastia appears due to three main causes: lack of male sex hormone testosterone, increased the creation of the female sex hormone estrogen, or as a result of taking certain medications.
The lack of testosterone (and gynecomastia) can be found in the following diseases: testicles underdevelopment , Klinefelter's syndrome and testicular feminization. Increased excretion of estrogen may be due to several reasons: testicular tumors, bronchial carcinoma, persons who have operated hermaphroditism, but some ovarian tissue left that produces hormones, natural flourishing of the adrenal glands, hyperthyroidism, adrenal gland tumor and liver diseases. Drugs can cause gynecomastia in several ways. Many drugs act directly as estrogens or increase its activity, for example men who take dietilstilbestrol for the treatment of prostate cancer and transsexuals who are preparing for the change of sex. Other drugs that may cause gynecomastia include: ketoconazole, digitalis, spironolactone, cimetidine, busulfan, etionamid, Isoniazid, Methyldopa, tricyclic antidepressants, penicilamin, Omeprazole, ACE inhibitors, diazepam. Marijuana and heroin can also cause gynecomastia.
Treatment
If the real cause can be discovered, by its treatment gynecomastia is often withdrawn. For example additional testosterone treatment in men with inadequate testicular function leads to a dramatic reduction in gynecomastia. Rare patients with painful gynecomastia, which is for any reason can not be cured by any other method is possible to be treated by anti-estrogen (tamoxifen).
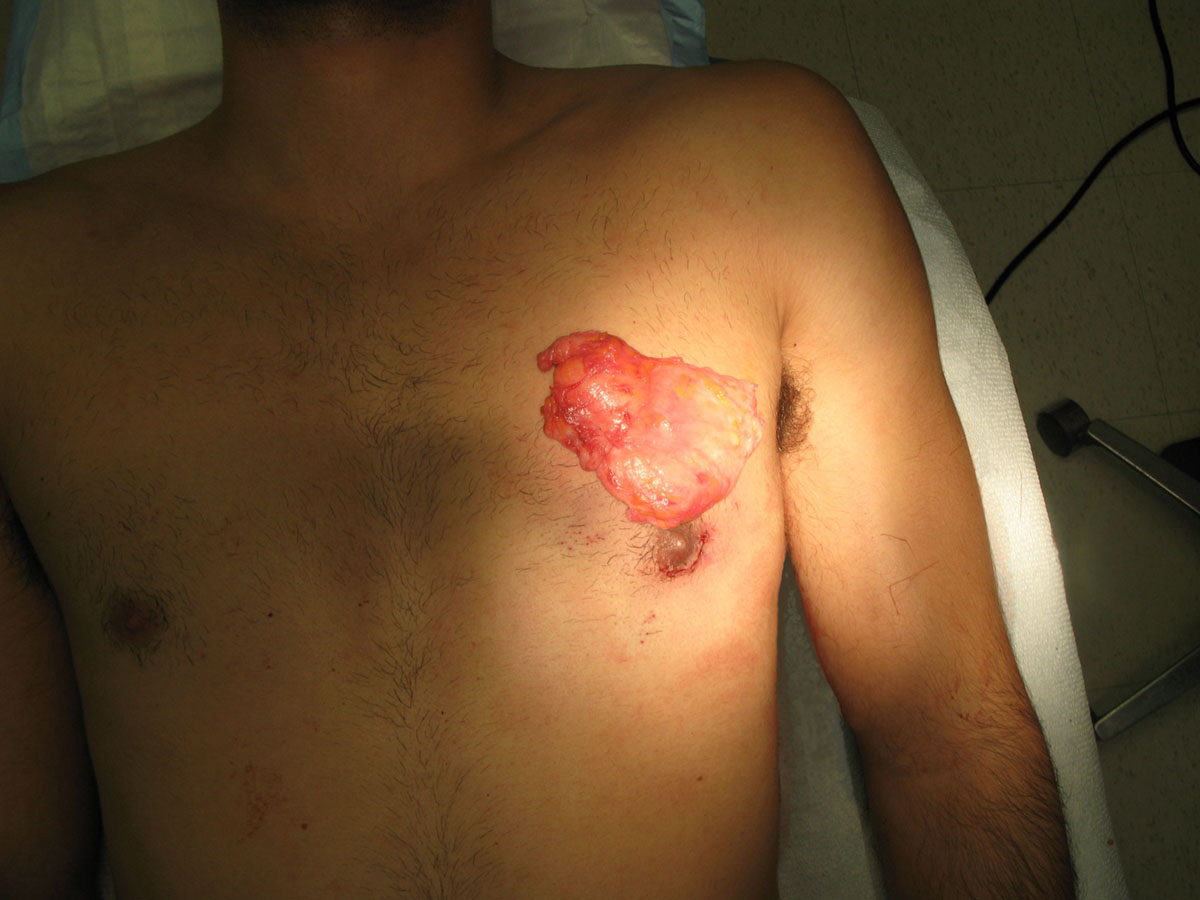
Surgical intervention of male breast reduction is recommended if the man has the aesthetic or psychological problem, if the breast is constantly growing, or malignant tumor in male breast is suspected. For most men in whom the cause of gynecomastia can not be treated corrective surgery is the solution. Unlike the radical breast reduction surgery in women, in men this procedure seems much simpler more like liposuction with small and unnoticeable cuts. Surgery performs under local anesthesia and takes about 90 minutes. Recovery takes about 6 weeks.
Complications
The postoperative course was accompanied by certain pain, swelling and hematomas. Appearance of infection is rarely. Late complications may be depression in the chest area due to removed too much fat or glandular tissue.
However, gynecomastia can be more serious problem than deteriorate look. It can be a sign of testicular or adrenal gland tumor or liver disease. Any unusual breast increase in men should therefore be examined by the doctor. Gynecomastia increases risk of breast cancer.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...