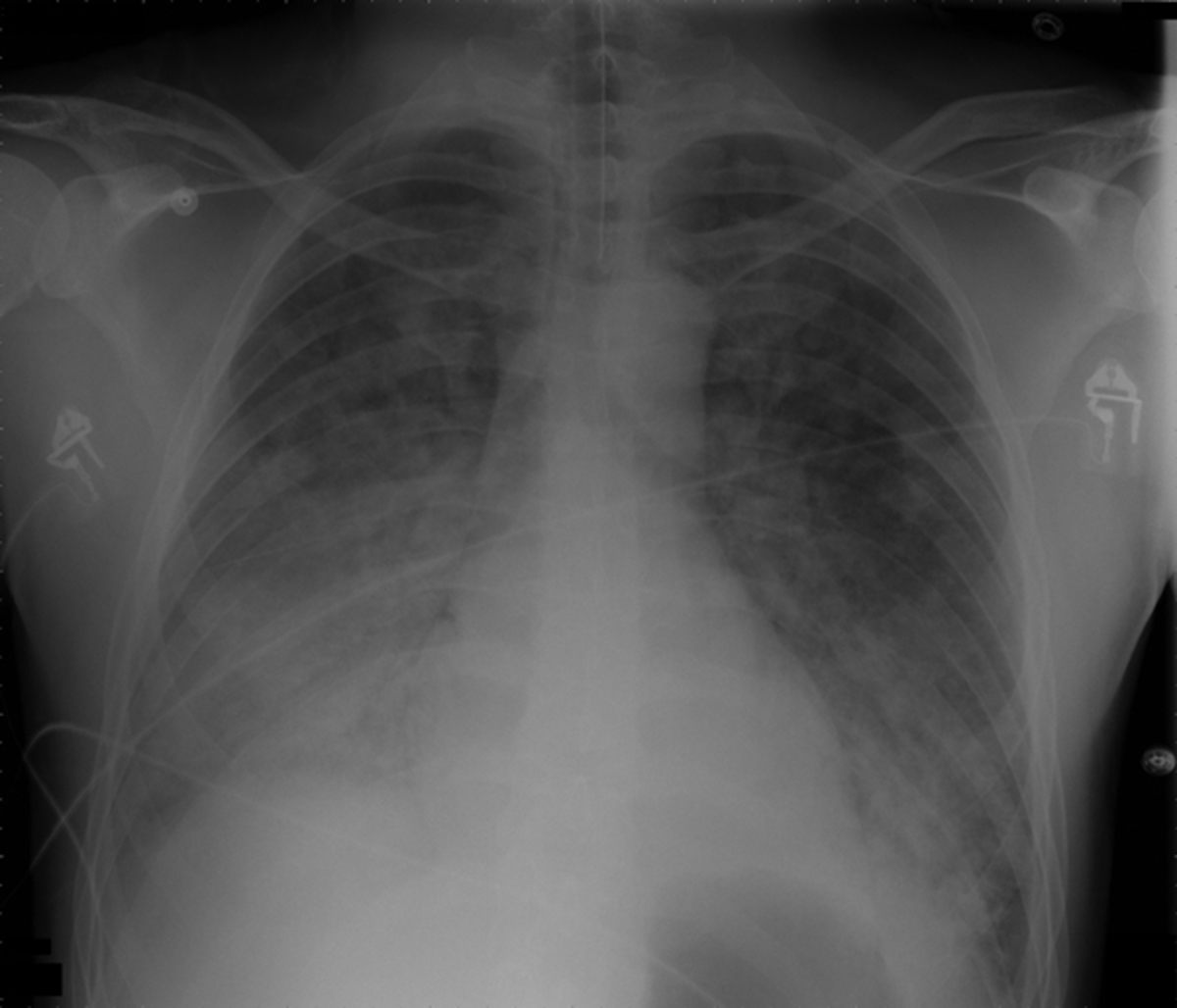
Croup also known as laryngotracheobronchitis is an acute infection of upper parts of respiratory tract caused by viruses. Parainfluenza virus is most frequent culprit of croup. Even some bacteria such as Corynebacterium diphteriae may lead to this infection. The symptoms of this condition vary in range from mild to rather severe. It presents with distinguished symptoms such as cough that resembles barking, stridor which is high pitch sound that occurs when the air passes through upper parts of respiratory tract in turbulent manner, and hoarse voice. Respiratory distress is common as well. Croup mostly affects children between 6 months and three years of age.
Complications
The complications of croup are not so usual. Still some of them may occur. The most present complication is secondary infection. It presents with pneumonia. Pneumonia may be viral or bacterial. Dehydration is another possible complication.
The severe cases of croup needs to be hospitalized. This particularly refers to prematurely born children as their respiratory track is not fully developed.
One more serious complication is a blockage of airways. This life-threatening condition known as respiratory distress requires immediate care and the child' breathing is supported by a ventilator. Prior the ventilator doctors can intubate the patient and if this method does not improve breathing one is definitely it can be supported by the ventilator.
Decreased amount of oxygen is another possible complication. It features with blue coloration of child's mouth which is called cyanosis. This complication is also severe and has to be dealt with in hospital.
Treatment
As viruses are mostly responsible for the condition there are no medications that will act against these infective agents. The disease will go away on its own rather soon.
The child is anxious because he/ she cannot breathe properly. Mothers are supposed to comfort them and place them into sitting position to improve breathing. No medications that may lead to drowsiness are supposed to be given as they will only make the situation worse.
In case of complications and after the admission into the hospital the child is firstly given oxygen. Corticosteroids are applied in order to reduce the edema of upper respiratory tract and improve breathing. The cases of dehydration which is a frequent complication of the disease are treated by intravenous fluids. It is good if a child can drink as this way the hydratation can be improved by both drinking and intravenously applied fluids. Fortunately even the most severe cases are cured and the child recovers completely.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...