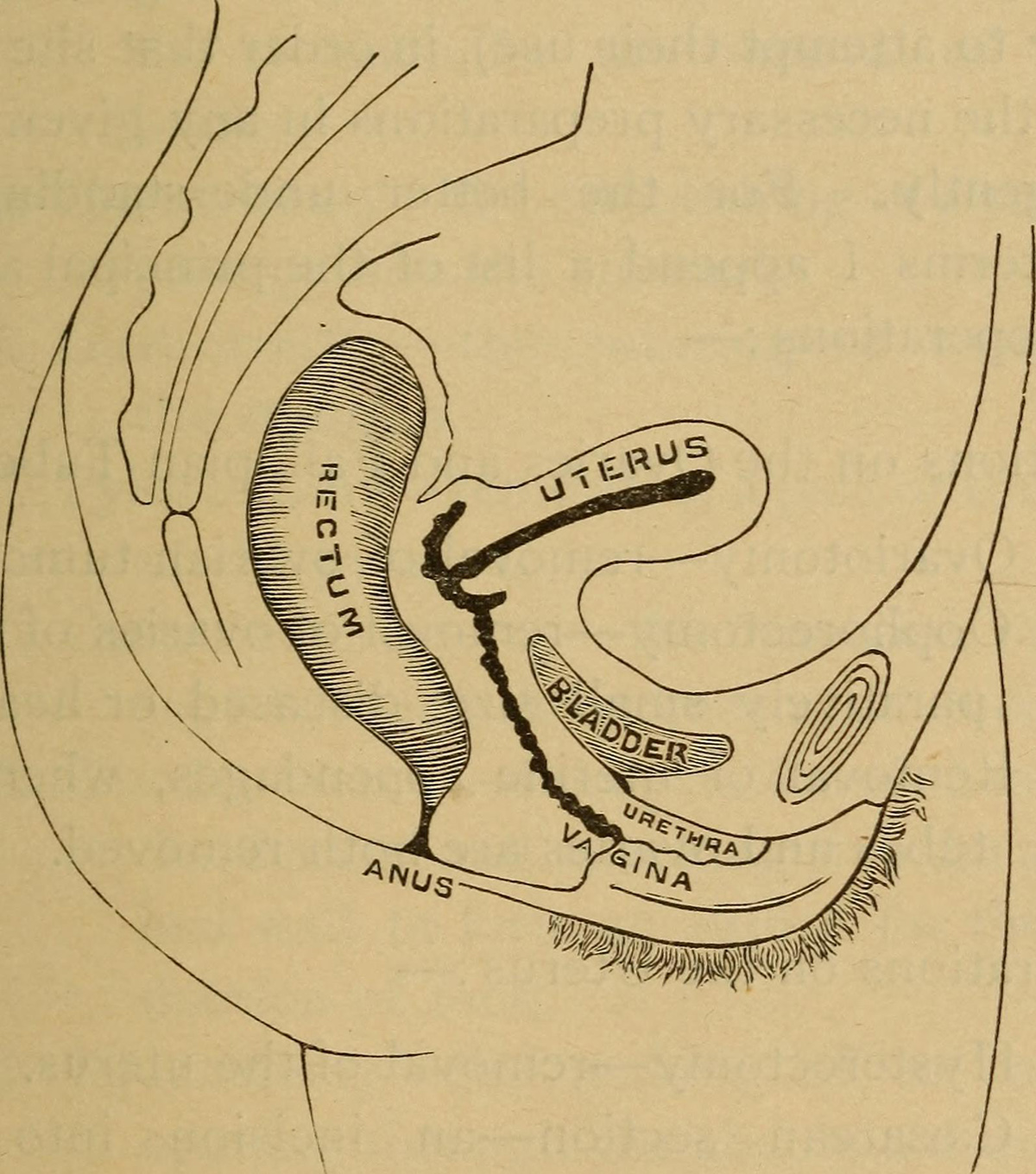
Oophorectomy is a surgical procedure in which one or both ovaries are removed. Ovaries are parts of female reproductive system and they contain eggs and they produce hormones which are in charge of the menstrual cycle. In most cases oophorectomy is necessary because of the disease such as cancer, cyst, torsion of the ovaries or endometriosis. Oophorectomy is commonly done together with other surgery such as removing of the uterus or removing of the fallopian tubes. In case if only one ovary was removed, a woman will menstruate and she will be able to have children. If both ovaries were removed, menstruation stops and a woman will not be able to have children.
Some of the complications which can occur after oophorectomy are infection, bleeding, damage of the surrounding organs, damage to the tumor which can cause leakage of the cancerous cells and retention of the ovarian cells which can cause pain.
Premature menopause can affect women who are close to menopause and had both of their ovaries removed. Since the production of hormones has stopped, there can be complications which includes the common symptoms of menopause (dry vagina and hot flashes), reduced the sex drive, depression, anxiety, difficulties with memory, osteoporosis, cardiovascular problems and premature death. However, menopause which is a consequence of natural aging process is different from surgically induced menopause because ovaries still produce low dosages of hormone after the menopause, but if the ovaries have been surgically removed, the production of hormones ends. The risk of these complications may be decreased if a woman takes hormone replacement medications. Osteoporosis may occur due to the lack of hormones which are responsible for normal bone density.
Oophorectomy is performed under general anesthesia. The doctor can make one large cut in the abdomen which provides access to the ovaries. If the doctor performs laparoscopic surgery, he/she will make several small cuts in the abdomen. A tube is inserted through the cut which has a camera (a laparoscope). The surgeon will separate the ovaries and the fallopian tubes and remove them through the other cut. After laparoscopic oophorectomy the recovery is faster, the patient can go home sooner and she will not have much pain. However, there are some cases in which this procedure cannot be performed. Depending on the woman's condition, she can leave the hospital after a few days. The recovery time depends on many factors but in most cases the woman will completely get better after six weeks at most.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...