Ribs are long and curved bones, and together with the breast bone and thoracic vertebrae, they form the rib cage. They are rather strong and too strong to be broken. However, under certain circumstances even a fracture of ribs is possible.
Causes of Broken Rib
Ribs most commonly break due to direct impact or repetitive trauma. The direct impact and subsequent rib fracture develop as a consequence of motor vehicle accidents, falls, and in-contact sports. It may also be associated with child abuse. Repetitive trauma and rib fracture are related to certain sports, such as baseball, basketball, or rowing. The ribs may be also broken due to severe and prolonged coughing spells.
Symptoms of Broken Rib
Patients whose rib is broken, usually complain about intensive pain in the chest, which tends to become even more severe when taking a breath and shows tenderness of the injured area. If the bone fragments go one across another, a specific sound called crepitus occurs. This crunchy sound develops as a consequence of dislodging of the bone fragments.
The person simply cannot breathe properly because of the pain. This may eventually cause the build-up of mucus inside the lungs and lead to pneumonia. Pneumonia is only one possible complication of broken ribs. In case a broken rib injures the pleura or even punctures the underlying lung, pneumothorax occurs. Fragments of broken bones may, in severe cases, cause internal bleeding.
Diagnosis and Treatment from Broken Rib
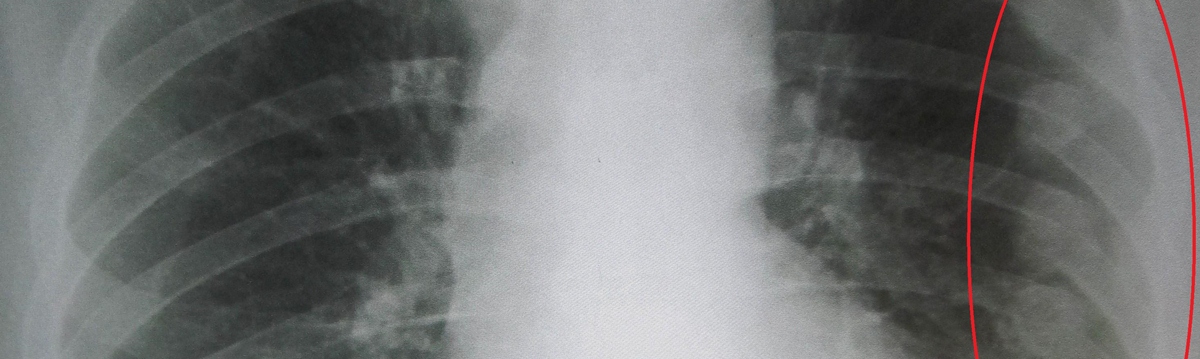
The person reports an injury, and the doctor performs a thorough physical examination. What follows is a chest x-ray which can perfectly visualize fracture and even certain complications such as pneumothorax.
- Patient with rib fracture suffers from pain, especially on inspiration or during movement. Other symptoms include tenderness and shallow breathing. A portion of thoracic wall moves separately from the rest of the chest (flail chest). There is a grating sound during breathing or movement. Rib fractures may also indicate more serious injuries in elderly people. Patients also exhibit symptoms of anxiety, restless or fear. They may complain of headache, feel dizzy, tired or sleepy.
- Chest x-ray remains the most effective method of diagnosing rib fractures. Approximately 25% of them do not show on x-ray and are diagnosed upon physical examination. Rib fractures are problematic because normal breathing causes pain.
- Eight different plain radiography pictures of ribs were performed with the patient in an erect position. The following projections were obtained in sequence: oblique at 45° or 30° angle on inspiration, oblique at 45° or 30° angle on expiration as well as 45° and 39° projections during slow and fast breathing. All radiographic examinations were performed using a Philips three-phase scanner installed at the Al- Razi Hospital in Jenin, Palestine.
- The results demonstrate that the 45° antero-posterior oblique projection performed on expiration is recommended for diagnostics and interpretation of traumatic rib fractures.
In case of rib fracture, the injured area is never placed in a cast. The cast will only restrict the movement of the chest and interfere with the normal process of breathing. However, to prevent further damage and to allow the broken rib to heal properly, one is supposed to have plenty of rest.
Reduction in movement will also reduce the pain. Broken rib in all cases leads to severe pain, and this is why patients are always prescribed pain-relieving medications. The pain is, in the majority of patients, alleviated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (ibuprofen and naproxen). Even though it may be difficult, one is advised to take deep breaths. This way, the entire lung tissue will ventilate properly, and the risk of pneumonia will decrease.
Treatment of pneumothorax may require hospitalization depending on its severity. Hospitalization and special medical care are also required if a rib fracture is associated with coughing blood, confusion, dizziness, and severe shortness of breath.
- www.nhs.uk/conditions/broken-or-bruised-ribs/
- www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/rib-injuries
- Photo courtesy of James Heilman, MD by Wikimedia Commons: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Fracturedribsmarked.jpg











Your thoughts on this
Loading...