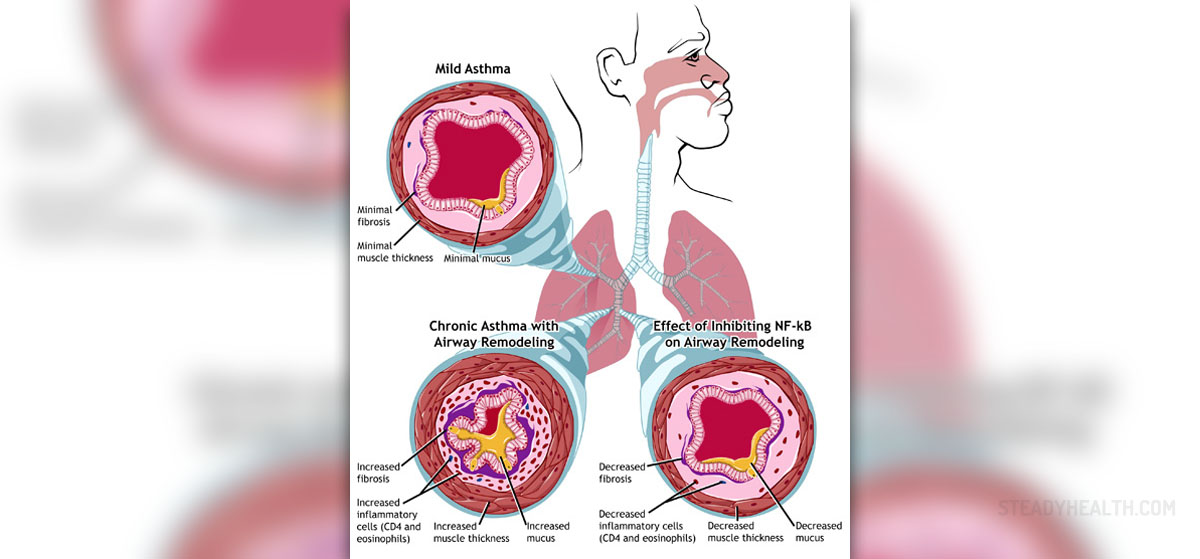
Chronic upper back pain can be a debilitating and, needless to say, painful condition. Even the most basic of activities can become uncomfortable. With upper back pain, you might experience numbness, tingling, radicular pain, weakness and lack of mobility. The word chronic refers to the fact that the condition has been persistent for at least three months.
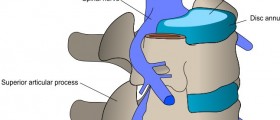
When we use the term ‘upper back’, we refer to the cervical spinal region, from C1 to C7. These vertebrae are vital for a number of reasons: they control head movements and also serve as a resting place for the head itself. Essentially, they are the support for the head. C1 is known as the atlas vertebrae, and C2 is known as the axis. The former rotates upon the latter. Pain in this area often originates in the neck and spreads to the shoulders, arms and hands.Symptoms
Symptoms pertaining to upper back pain normally come about as a resultof muscle or ligament sprain. This usually occurs in the neck or upperand middle back. Generally, this kind of pain occurs due to repetitiveactivity or poor posture, and can normally be controlled by using overthe counter painkillers. If these symptoms last more than three months,the condition is considered chronic. If chronic pain occurs, it ispossible that the anatomical structure of the spine itself might becompromised. In this case, conditions such as osteoarthritis, bonespurs, bulging discs, herniated discs and spinal stenosis might bediagnosed.
Causes
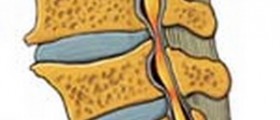
Chronic back pain might be caused by a herniated disc, which involves the rupture and leakage of a spinal disc. If an intervertebral disc becomes weak and protrudes from beyond its normal perimeter, this is known as a bulging disc, which is another potential cause of back pain. Bone spurs might also cause upper back pain, as can degenerative disc disease. Foraminal cervical stenosis is another condition that might lead to chronic upper back pain. This condition involves a narrowing of the cervical foramen.Treatment
In some cases, chronic upper back pain might require surgery. However, surgery should only be a last resort. Before one goes down that road, it might be advisable to first of all try anti-inflammatory medication, chiropractic work, stretching or steroid injections. If these options fail, surgery might be the only remaining choice - however, it should be remembered that surgery can involve long recovery periods and risk of infection.



-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...