What is bulging disc?
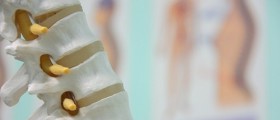
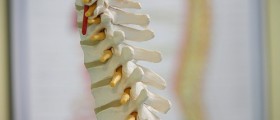
A bulging disc is a common name for a contained spinal disorder, and that is a condition where the intervertebral disc bulges towards the spinal canal. Let us explain these terms before we go on. The spine of all animals that has a skeleton - humans among them - is made up of a number of vertebrae. These are bones with a main body, roughly cylindrical in shape, with arches and processes that protrude from it. Vertebrae are packed on top of one another, like a stack of coins.
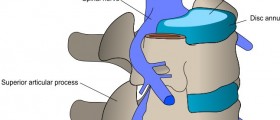
Of course, you know how spine is flexible. You can bend it in any direction. This is due to the special construction of joints that connect any two vertebrae. The center of the vertebrae is slightly concave (sunken) and there is a lens-like space between the main, weight-bearing bodies of any two neighboring vertebrae. this space is filled by a lens-like structure known as spinal disc. It is made of the hard and elastic outer layer and liquid, gelatinous inner filling. The discs serve as dampeners and also allow the vertebrae to slide in any direction in a single plane. Vertebrae are kept in place by several powerful ligaments.
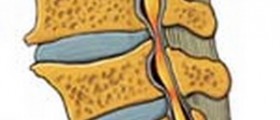
The trick with the spinal disc is that it is exposed to extreme stress. Motion dynamics of the body are such that the spine must withstand much greater loads when we move than our plain weight. They are also susceptible to wear and tear and damage by various medical conditions. the bottom line is that the outer layer of the disc may weaken enough for the inner gelatinous filling to protrude from it, or to leak out if the disc ruptures - a vertebral hernia. Discs can also slip out of their place, which usually happens when the degenerative processes in the spine, normally, associated with aging, allow for that to happen. This condition is known as bulging disc. What happens is that damage to the outer layer increases its permeability and allows the gelatinous substance in the center to "dry". The disc thus looses its shape, volume and elasticity, and vertebrae are drawn closer together. A failsafe mechanism then causes bone spurs of the affected vertebrae to grow, in order to immobilize the damaged region. These spurs can grow so much that they begin to fill the spinal channel and press on the spinal cord - a spinal stenosis.
Symptoms and diagnosis
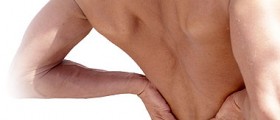
Symptoms usually depend on the location of the bulging disc. Pain and discomfort are felt in legs and hips if the bulging is is lower, and in the arms and shoulders if the affected disc is higher in the spine. The diagnosis is made through test results. Tests include X-ray, MRI and CT scans.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition and can be conservative, which includes rest and aid of painkillers if necessary, or can be done via physical therapy with the help of an expert physical therapist and epidural steroid injections.




-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...