Spinal stenosis is the medical term used to describe an abnormal narrowing of one or more parts of the spine. Such narrowing predominantly affects the cervical and lumbar spine. The condition results in compression and irritation of the spinal cord and sometimes also the spinal nerves. That, in turn, has the potential to lead to a whole range of different neurological problems including numbness, pain, muscle weakness, and incoordination of the affected extremities.
Spinal Stenosis in Middle Age
Spinal stenosis is much more likely to affect older patients, or in other words, this medical condition is commonly age-related. That is because the spine naturally undergoes a variety of changes as we get older. These changes generally affect the bones of the spinal column and protrude into the spinal canal, reducing the inner volume and subsequently triggering the above mentioned health problems and symptoms.
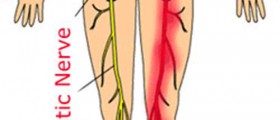
Except for the cervical spine, the lumbar portion is most commonly affected by age-related changes in the elderly population. For instance, the bony and soft tissue structures of the lumbar spine might become hypertrophic (increased in size). This precipitates the entrapment of the cauda equina roots, nerve bundles that affect the groin, hips, and legs. As a result, patients gradually start to feel incapacitating and excruciating pain in the lower back, which tends to radiate towards the lower extremities as well. Muscles become weak, and there are leg paresthesias like tingling and burning sensations. More complex cases are characterized by loss over bowel and bladder function, and sexual function can also be affected.
Osteoarthritis, disc degeneration, and thickened ligaments are the three most common causes of spinal stenosis in older individuals. Osteoarthritis, abnormally weak and brittle bones, generally affects the facet joints. The body's natural attempt to repair the damaged joints takes place in the form of new bony growths called bone spurs. These bone spurs protrude into the spinal canal and trigger stenosis.
In the case of disc degeneration, the disc per se may easily bulge or its jelly-like center can protrude into the spinal canal. This leads to the compression or irritation of the content of the spinal canal. And finally, once the ligaments holding the vertebrae together become thick enough, they may narrow the spinal canal and compress the nervous tissues inside.
Apart from the above mentioned causes of spinal stenosis, the condition may also affect middle aged people as well as young individuals. This typically happens if they are suffering from certain medical conditions or have had some kind of injury to the spine. Spinal stenosis is not uncommonly reported in younger patients living with Paget's disease of the bone, those suffering from achondroplasia (dwarfism), people with spinal tumors, and patients with a history of serious spinal injuries such as fractures or dislocation of one or more vertebrae.
As for treatment, it basically starts with medications like antidepressants, anti-seizure drugs or opioids, all of which are prescribed to people who experience excruciating pain. Patients with spinal stenosis additionally benefit from physical therapy and may receive steroid injections. Surgery is indicated only if other treatments fail to bring the symptoms under control, patients develop severe neurological deficits that do not resolve on conservative treatment and in those suffering from spinal tumors.
MRI for Spinal Stenosis Diagnosis
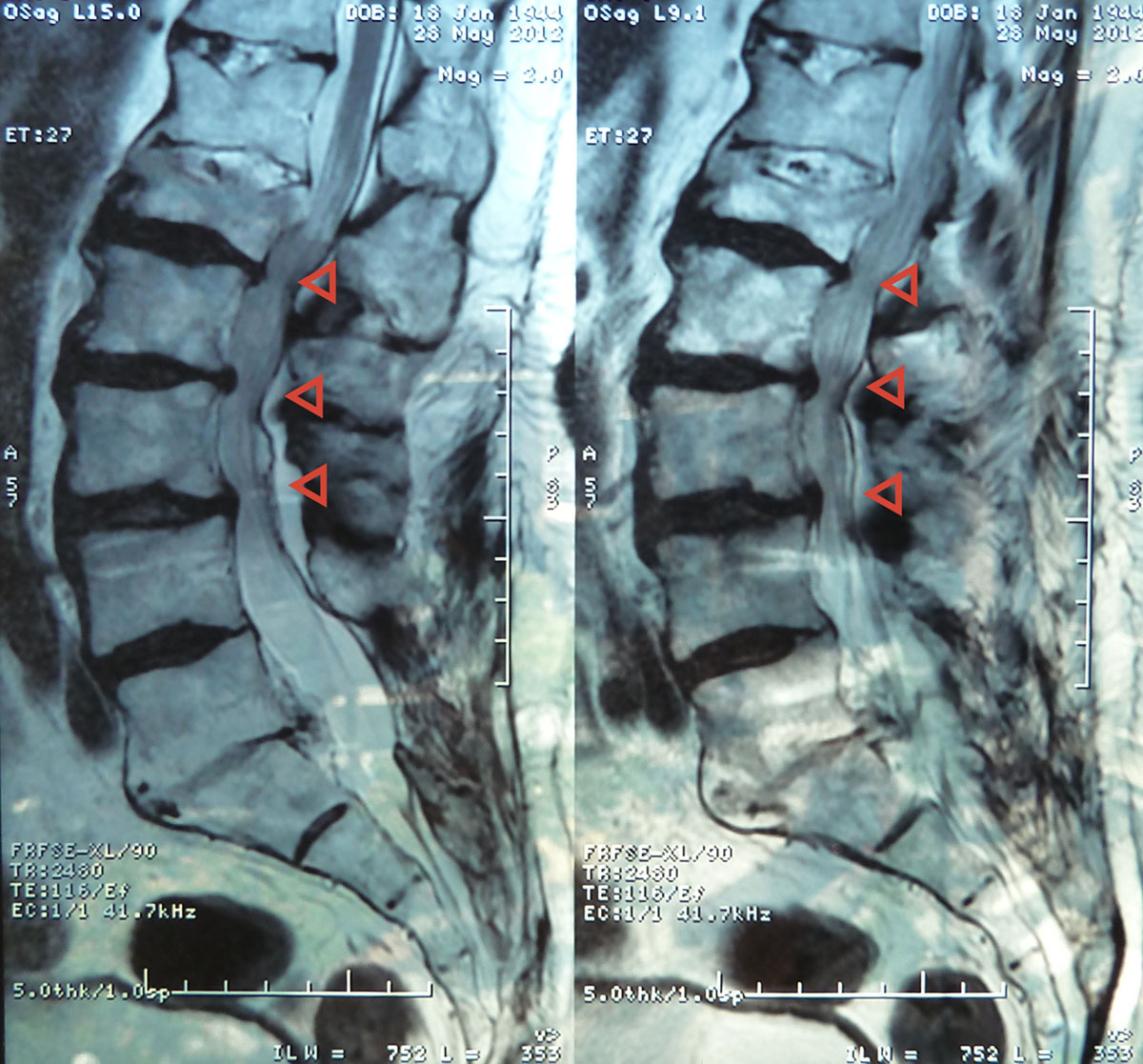
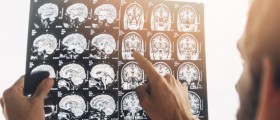
Diagnosing spinal stenosis goes through several stages. Initially, all patients are asked specific questions regarding symptoms they experience and then undergo physical and neurological exams. Radiographic confirmation of the condition is achieved with several imaging modalities. Depending on the underlying cause of spinal stenosis sometimes X-ray may be sufficient enough while in more complex cases doctors additionally indicate CT scans or MRI of the spine.
Plain films of the spine are efficient when it comes to confirmation of degenerative changes affecting bony tissue in the area. They are, on the other hand, practically useless when there are structural changes in the soft tissues. In such case CT can or MRI must be done.
Even though CT scans can perfectly visualize the subarachnoid space and spinal roots this is an invasive test which carries certain risks. For that reason doctors prefer using MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging is a powerful tool for visualization of soft tissues. It gives an excellent insight in various structures of the spinal area including the entire spinal cord along with the cauda equina (the terminal part of the spinal cord), ligaments, epidural fat, subarachnoid space and spinal discs. Typical characteristics of spinal stenosis are loss of epidural fat and cerebrospinal fluid. They both can be easily confirmed with MRI.
The procedure is done in the axial and sagittal planes. A well experienced radiologist can easily notice potential underlying diseases that have triggered spinal stenosis. He/she will confirm the presence of osteophytes, calcified bulging discs, changes in epidural soft tissues etc. Enhancement of the obtained images is achieved with intravenously administered gadolinium, a highly efficient contract agent indicated only in healthy patients i.e. those who are not suffering from any kidney disorder.
If we want to discuss the degree of confidence, scientists assure that MRI is practically the best diagnostic tool for spinal stenosis. So, most medical experts opt for this imaging technique as soon as they assume the person is suffering from spinal stenosis which cannot be properly evaluated with plain radiographs.
And finally, a false-positive test finding is a rare occurrence. False-negative results may occur more frequently but they are mostly related to movement artifacts.
All in all, spinal stenosis is a severe medical condition which in the long run may lead to permanent neurological sequelae. But if diagnosed in a timely manner with an MRI of the spine, and adequately treated, patients with spinal stenosis may fully recover and suffer no permanent damage.




_f_280x120.jpg)



_f_280x120.jpg)
Your thoughts on this
Loading...