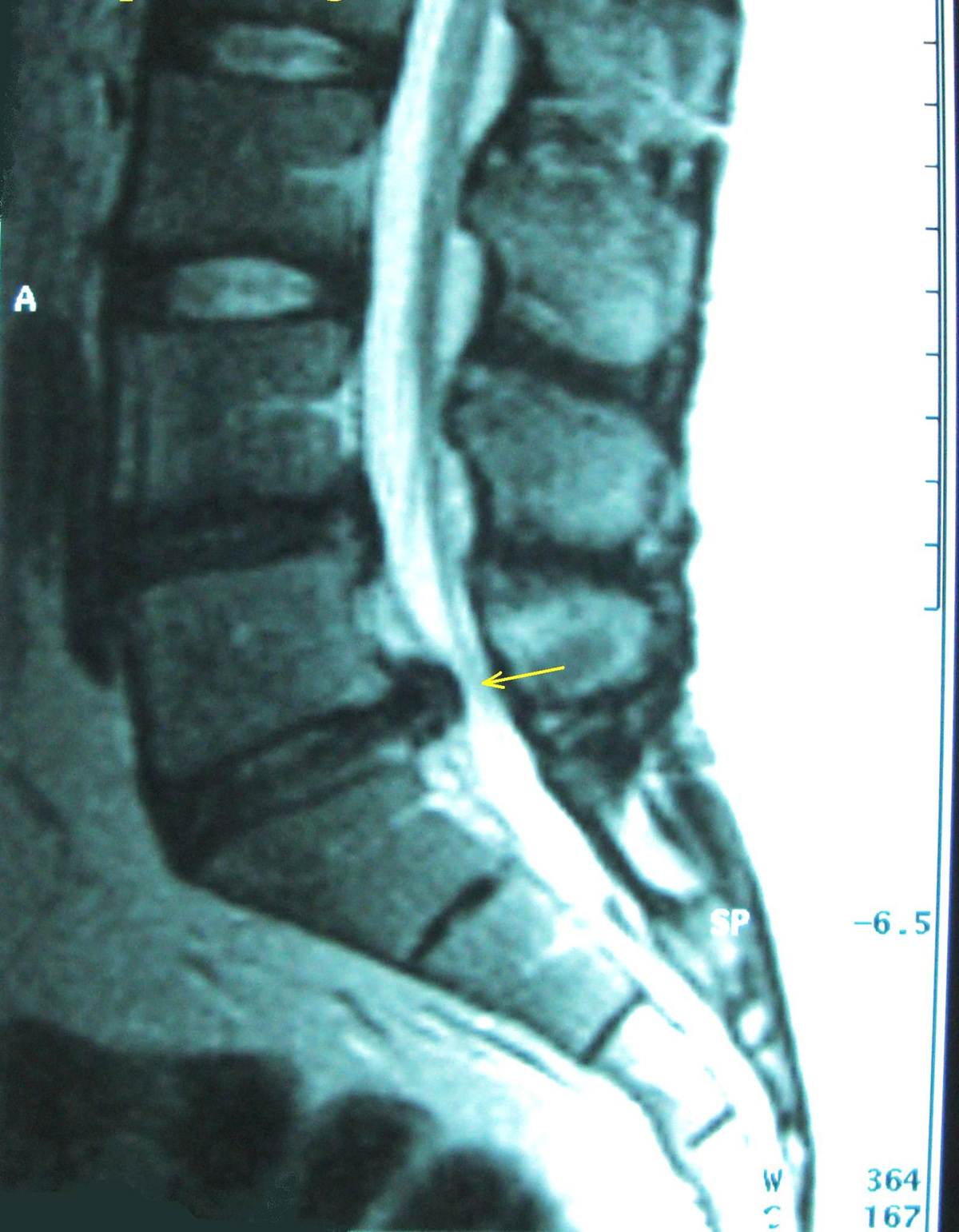
Spineand spinal discs
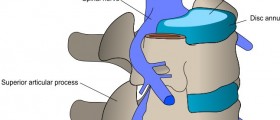
Spineor spinal column is the uniting element of the entire skeleton. Head,arms, legs and the ribcage are attached to it. Spine consists of anumber of cylindrical bones known as vertebrae, stacked on top ofeach other and connected by complex joints which allow the spine tobe both very strong and very flexible. Key of spine's strength thatgoes along with flexibility lies in the joints between the vertebrae.Vertebrae are held in place by powerful ligaments, and the spacebetween vertebrae is filled with structure known as disc. It is aconvex, lens – like structure which has a hard and elastic outerlayer and soft, gelatinous inner filling.
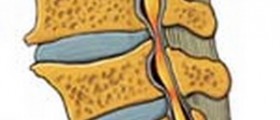
This disc serves both as acushioning device or dampener, and allows the vertebrae to be able toincline in any direction in their plane of motion. Spinal discs areexposed to great stress and are susceptible to wear and tear overtime, like all other structures in the body. In some instances,spinal discs can slip out of their place and bulge or protrude fromthe spinal column. This condition is popularly referred to as abulging disc. It moves for only a few millimeters, but enough tocause problems in some persons. If it happens that the bulge isexerting pressure on the nearby nerves in the spinal cord. This ismanifested in form of pain
Causesand symptoms
The spinaldisc gradually weakens and people who suffer from this condition aretypically the elderly. Wear and tear become more stressful to thedisc as its structure weakens and becomes less elastic. Activitiessuch as bending, sitting, and lifting of heavy objects can furtherweaken the disc, and so can something that seems harmless, as is pooror wrong posture.
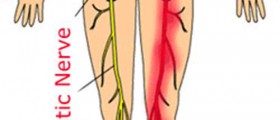
Symptoms depend on the location of the bulgingdisc. For example, if the bulging disc is in the lower back, the painis sharp and is felt at the place where the disc is bulging, andmight extend to the legs. Pain caused by bulging disc in the neck isfelt in the shoulders and arms. Intensity of pain depends on how muchthe bulging disc presses on the nearby nerves. Pain is usuallyfollowed by a sensation of tingling and numbness. Other symptomsinclude possible muscle spasms in the region innervated by the nervethat is being pressed, and the feeling of weakness of the involvedmuscles.
Treatment
Physicalexaminations and tests like X-ray and MRI scan are used to establisha diagnosis. The goal of the treatment is to relieve the pain felt assoon as possible. The patient must rest and avoid activities that cantrigger the pain. If the pain is severe, treatment by pain- andinflammation relieving medications becomes an option, and if thesymptoms persist, surgery becomes an option.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...