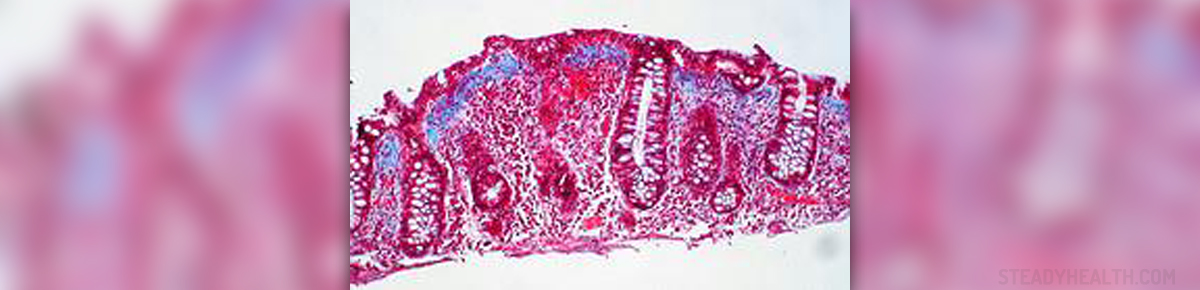
Colitis is an inflammation of the colon. The chronic type of colitis is persistent, and broadly fit into the category of digestive diseases. Collagenous colitis is a type of chronic colitis defined as an inflammatory disorder of the colon that causes persistent watery diarrhea. This type of colitis usually affects women in the 5th decade of life. It is often classified under the umbrella entity microscopic colitis usually characterized by chronic watery diarrhea, normal colonoscopy (the endoscopic examination of the colon) and characteristic histopathology. The examination of the tissue unveils an increase in inflammatory cells with an otherwise normal appearance of the colon. A thickened subepithelial collagen layer is also present, and it may become up to 30 micrometers thick. The diagnosis is established after reexamining the small tissue sample using a microscope.
Symptoms of chronic colitis
The most prominent symptoms of colitis in clued problems with chronic watery diarrhea, pain in the stomach region, abdominal cramps, excessive weight loss, nausea and fecal incontinence. The exact signs and symptoms of chronic colitis are dependent on the exact cause of the given inflammation, and many other factors that may influence the severity of symptoms. Patients will typically feel very tired, may experience bloating, changes in bowel habits, fever, and distension. Colonoscopy is usually normal, or near normal. Only some slight redness of the inner surface of the colon is to be expected. However, medical attention is needed in all cases where watery diarrhea persists for a couple of days.
Causes of chronic colitis
The exact cause of collagenous colitis is largely unknown. However, there is some evidence that non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as diclofenac for example, may contribute to the development of this disease. It may also occur after prolonged use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, which are often used as antidepressants in treatment of many psychiatric diseases (depression, anxiety disorders and personality disorders). Bacteria and viruses that irritate the lining of the colon are also considered as possible causes of this disease. It is also speculated that chronic colitis develops as an autoimmune disorder that occurs when body’s immune system attacks healthy tissues.
Treatment for chronic colitis
Simple lifestyle moderation is often the best way to fight with chronic colitis. Patients are advised to eat low fat and low fiber diet to help relieve diarrhea. It is also important to stop using certain medications such as NSAID pain relievers, which are typically available over-the-counter. Doctors may also recommend anti-diarrhea drugs, drugs that block bile acids, steroid medications to stop inflammation, immune-suppressants and anti-inflammatory drugs.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...