
A virus is a pathogenic microorganism capable of causing a variety of infections and diseases. Once it enters the body, the virus starts to multiply rapidly leading to worsening of the infection it causes. Also, a viral infection that affects one part of the body can spread to other body parts through circulation of the blood. The heart can be also affected by a viral infection. Such infection can cause heart disease which can weaken the heart and interfere with its function. This can result in many cardiovascular problems such as viral cardiomyopathy. Viral cardiomyopathy is one of diseases caused by viral infection of the myocardium (the cardiac muscles).
Causes of Viral CardiomyopathyInfection caused by a virus known as coxsackie virus B is one of the most common causes of this type of cardiomyopathy. This virus infects the myocardial sac and cardiac muscle which results in inflammation of the heart muscle. The disease weakens the heart and it cannot pump efficiently.
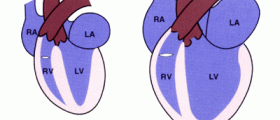
The most common form of viral cardiomyopathy is dilated cardiomyopathy, characterized by enlarged atria and ventricles of the heart. Ischemic cardiomyopathy is a type of viral cardiomyopathy that can lead to heart failure. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is another form of cardiomyopathy which causes the left ventricle to enlarge resulting in poor pumping of the heart.
Symptoms of Viral CardiomyopathyIn most patients the disease is asymptomatic and even those who show signs of cardiomyopathy have very subtle symptoms. Initially, viral infection of the myocardium does not cause any symptoms. However, as the disease progresses the symptoms start to appear.
The most common symptoms of viral cardiomyopathy is chest pain that may spread to the shoulder and arms. Palpitations or abnormal heart beat are also common and may appear similarly to palpitations during a heart attack. Excess fluid leads to enlargement of the heart and swelling of the extremities.
Viral cardiomyopathy can also cause shortness of breath, feeling of fatigue and tiredness even with minor physical strain. Dizziness and lightheadedness are often present too. Additionally, viral cardiomyopathy can be accompanied by formation of blood clots, heart murmur and unexplained weight gain.
Treatment for Viral CardiomyopathyViral cardiomyopathy can be diagnosed with the help of diagnostic tests such as electrocardiogram, MRI or CT scan. Treatment for viral cardiomyoapthy aims to clear away the infection and relieve the symptoms. The disease is commonly managed with diuretics, anticoagulants and medications for palpitations. Rarely, surgical treatment may be needed to remove parts of the heart and manage the disease. If the patient does not respond to any of these treatment options, heart transplant may be considered.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...