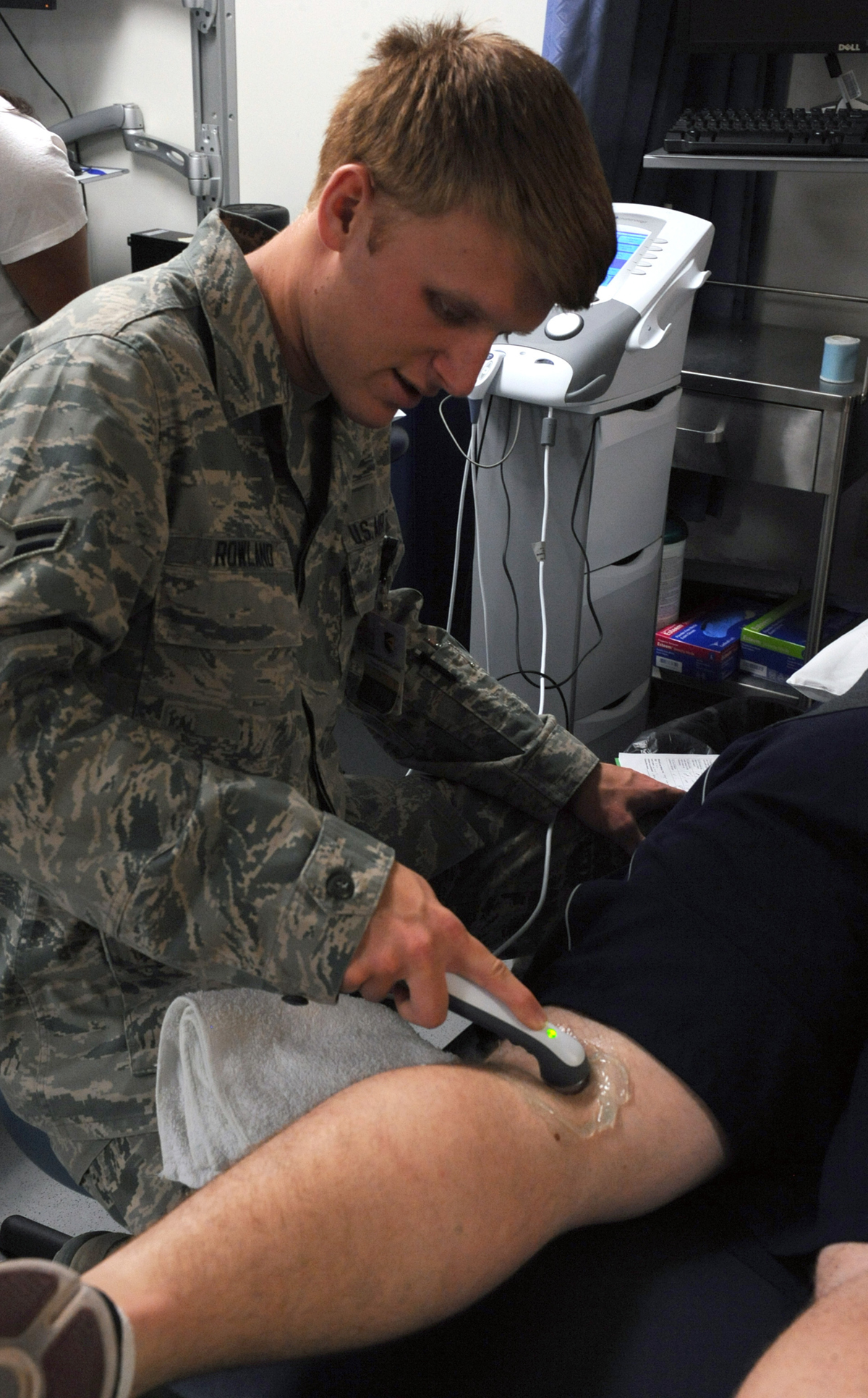
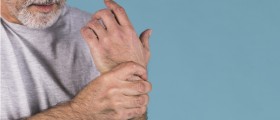
Muscle spasms — in which a muscle tenses and cramps spontaneously — may be acute and they can also appear in a chronic form. If muscle spasms become chronic, they may cause pain and interfere in a person's everyday activities.
Muscle spasms generally occur due to the overuse of the muscles, or they are associated with muscle tear and strain. Dehydration or an imbalance in electrolytes are two other frequent causes of muscle spasms. Even something as simple as not warming up before exercising can lead to muscle spasms.
Every muscle in the body can be affected by spasm. People who have to deal with chronic muscle spasms are advised to consult a doctor in order to receive proper treatment. The underlying cause of chronic muscle spasms must be identified.
Common causes of chronic muscle spasms
As already mentioned, chronic muscle spasms are most commonly associated with overuse of the muscles. An excess of strenuous exercise can exhaust your muscles (causing muscle fatigue), and this can eventually lead to an inability of the affected muscle to contract and relax properly.
Another common cause of chronic muscle spasms is atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaque builds up on the inner walls of the arteries. In atherosclerosis, the muscles are simply not well supplied with oxygen and other nutrients due to a narrowing of the blood vessels.
Chronic muscle spasms are also characteristic of certain systemic illnesses such as diabetes, anemia, and multiple sclerosis. In diabetes, the patient suffers from improper circulation which affects many organs, including the muscles. Anemia, the state of a low amount of hemoglobin, hinders the transfer of oxygen. If muscles do not get an adequate amount of oxygen, spasms occur. And finally, in multiple sclerosis, there is a damage to the nerves which innervate specific muscles. Damage to the nerves may lead to the occurrence of spasms.
Dystonia is a neurological condition, where you suffer from sustained muscle contractions and subsequent twisting and repetitive movements and abnormal posture. You can also have chronic muscle spasms.
It is estimated that chronic muscle spasms most commonly occur in the lower back. Chronic muscle spasms in the lower back tend to be induced by overworking the low back muscles and not allowing them rest.
Treatment for muscle spasms
Chronic muscle spasms generally lead to muscle soreness and pain. In the majority of cases, patients would be recommended to have plenty of rest. The rest is not supposed to last longer than a few days, since regular but light physical movement helps.
A person may deal with muscle spasm by increasing a certain physical routine gradually. Furthermore, if one's physical activity leads to muscle spasms, it can be replaced with an easier or less intense activity.
In people who have already suffered from muscle spasms, there is an increased chance for spasms to reoccur. To prevent the recurrence of muscle spasm, one may perform simple exercises such as stretching in order to increase the flexibility and elasticity of the joints and muscles.
The affected muscle can be wrapped in a comfortable bandage as it heals. This can successfully prevent internal muscular bleeding and the onset of repeated series of muscle spasms. And finally, there is one more way how to deal with muscle spasms. Home remedies for muscle spasms and cramps include relaxation techniques. Massage, heat therapies, and cold compresses are not supposed to be applied during the very attack of muscle spasm. They may be applied only after the spasms have subsided.
If you suffer from repeated muscle spasms, it is advisable to seek medical care for proper diagnosis and, where relevant, treatment. Should your muscle spasms not be caused by simple overexertion but instead by an underlying medical condition, you will want to be aware of the cause, so that you can receive treatment or learn how to best manage your muscle spasms.












-Causes,-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...