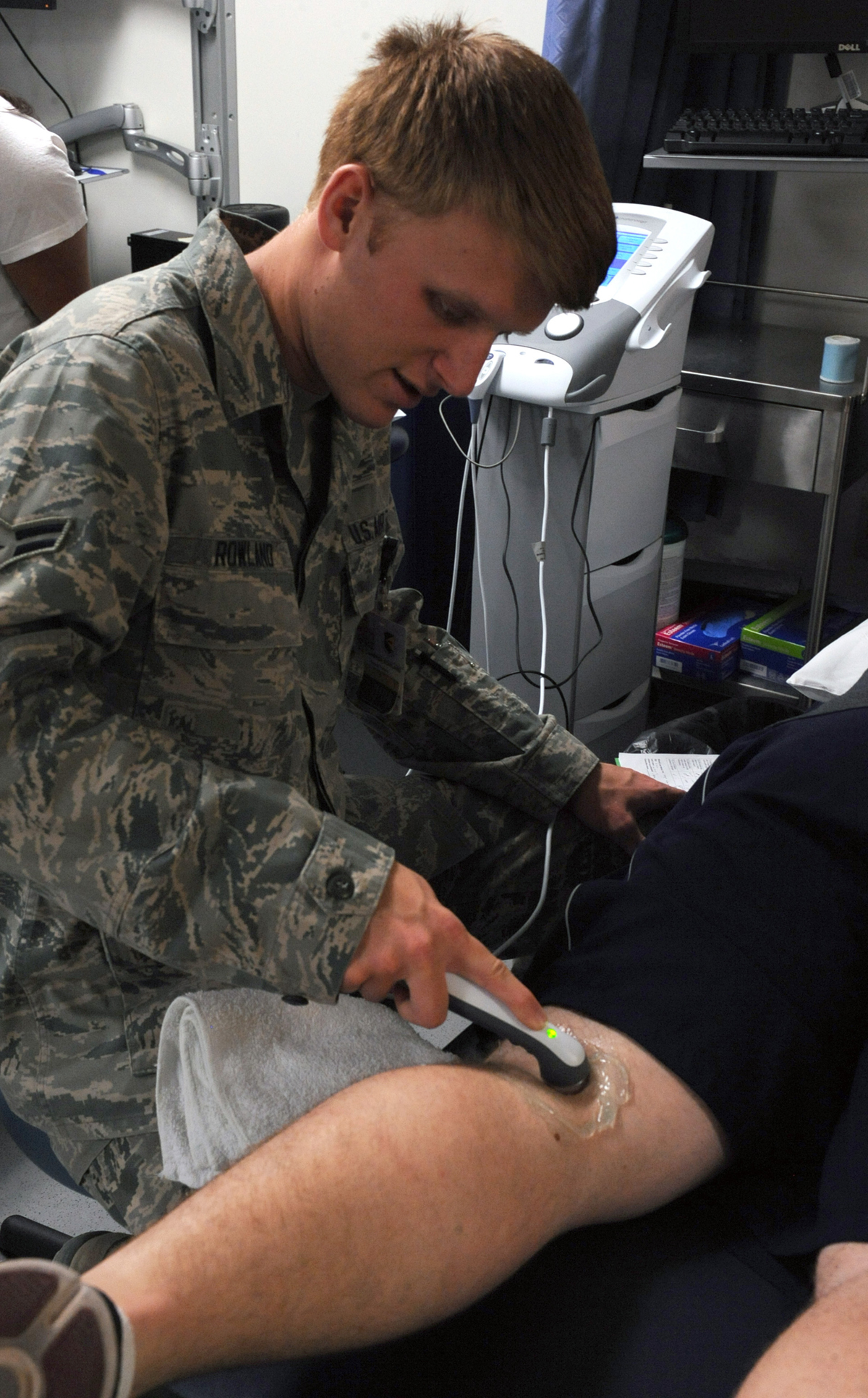
General Information about Muscle Spasms
A muscle spasm can be defined as an involuntary muscle contraction. It can affect one muscle, the entire group of muscles or muscles from different anatomical groups. The spasm develops suddenly without previous warning symptoms and signs. It can be painless or accompanied by pain of different intensity. It is essential to differentiate a muscle spasm from a muscle twitch. A muscle twitch represents a fine movement of a small portion of the muscle that can be easily seen under the skin.
There are many different causes of muscle spasms. Muscle spasms are, for example, typical for overused and overstretched muscles. Overuse of muscles and subsequent muscle spasms are, therefore, typical of athletes as well as people of certain professions such as construction workers. Furthermore, muscle spasms may point to electrolyte imbalance. Lack or excess of certain electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium may induce muscle spasms. The condition also occurs in case of severe dehydration.
Atherosclerosis is another possible cause of muscle spasms. Namely, narrowing of the peripheral arteries induces muscle spasms of the extremities due to improper blood supply. Muscle spasms can also be a characteristic of some systemic illnesses. They include diabetes, anemia, kidney disease, problems with the thyroid gland and hormonal imbalance. And finally, muscle spasms develop due to many neurological illnesses such as multiple sclerosis, dystonia, stroke as well as spinal cord injury.
Therapy for Muscle Spasms
Because there are many causes of muscle spasms it is clear that treatment will basically depend on the particular underlying cause. Athletes as well as people who perform certain activities associated with overuse or overstretching of muscles should pay attention and spare particular groups of muscles from excessive strain.
Dehydration and electrolyte imbalance require proper intake of fluid and specific treatments. Namely, if there is a lack of certain electrolyte it must be administered and excess of the electrolyte requires its assisted elimination from the body.
Systemic illnesses such as diabetes and atherosclerosis require proper treatment and once the condition is brought under control muscle spasm will withdraw. In case of neurological illnesses muscle spasms may not completely withdraw but they can be well-controlled with medications that treat the underlying condition or such patients benefit from specific drugs that control the very contraction of the muscles. Muscle relaxants are drugs able to control muscle function and decrease muscle tone. They are quite efficient in alleviating symptoms such as muscle spasms or muscle pain. The doctor chooses the most convenient medications and some patients are successfully treated with a combination of several drugs.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...