The lungs are vital organs that provide with proper exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Their structure and anatomy is rather specific and complex. In humans the trachea branches into two main bronchi, right main bronchus and left main bronchus. These bronchi enter the lungs and what follows is further division of the bronchi into smaller bronchioles which eventually end up as the alveolar sacs. Alveolar sacs are the most significant part of the lungs since they represent the exact place of oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange.
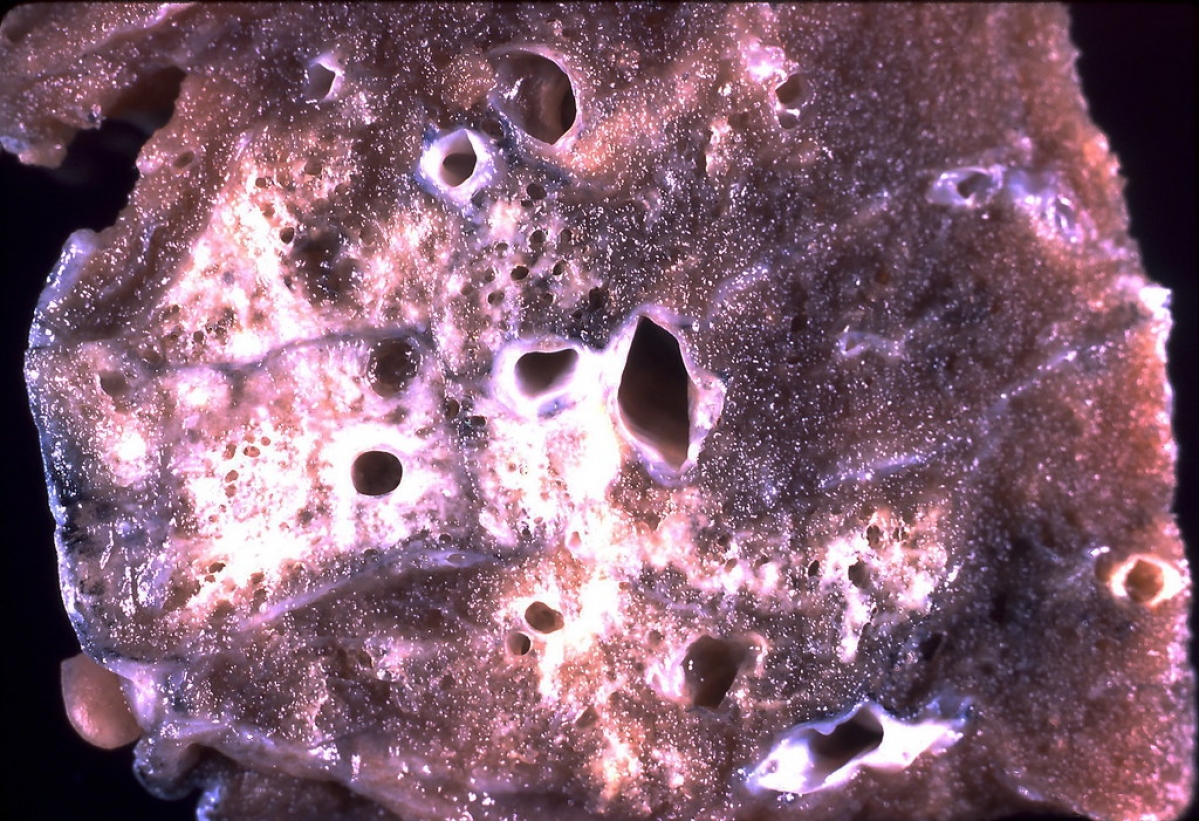
In lung infection any of the previously mentioned structures may be affected and the very process of inflammation causes noticeable symptoms and signs of the infection and interferes in proper supply with oxygen.
Causes of Lung Infection
Lungs are naturally moist which makes them susceptible to infections. There are many infections of the lungs and they basically vary according to the infective agent that has caused the infection. Both bacteria and viruses may lead to lung infection. These pathogens are inhaled with the air and if not properly eliminated or in case the immune system does not function normally microorganisms settle in the lungs, start to multiply and cause inflammation.
Some people are more prone to lung infections. They include all those patients suffering from chronic illnesses (heart conditions, COPD etc.) and those with weak immune system. Even patients who are bed ridden for longer period of time easily develop lung infection. Heavy smokers are at higher risk of lung infections. And finally, lung infection may be induced by occupational and environmental factors such as long-time exposure to a variety of pollutants and toxins.
Symptoms and Signs of Lung Infection
Since there are numerous lung infections there is a variety of symptoms and signs. In general all infections are accompanied with certain level of lung tissue inflammation which consequently results in specific symptoms and signs.
Cough is generally a characteristic of all infections. It can be dry or productive. In tuberculosis the sputum may contain blood. Inflammation leads to increased production of mucus and secretions. Excessive production of mucus and secretions as well as swelling of the nearby tissue of the alveoli and broncheoli interferes in respiration. This eventually results in shortness of breath. Furthermore, patients may complain about chest pain or discomfort, wheezing or stridor and in serious cases of oxygen shortage the patient may develop cyanosis. All lung infections cause general weakness, loss of appetite and consequent weight loss. In some cases of lung infections patients may develop fever and chills. And finally, the symptoms of the infection tend to get worse at night which may significantly interfere in sleep and cause exhaustion.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...