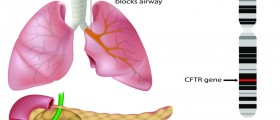
Cystic fibrosis is a chronic and progressive illness. It is a genetic disease that affects mucus glands. The changes associated with cystic fibrosis affect the respiratory and gastrointestinal system, to be precise certain parts of gastrointestinal system. The sweat glands are affected as well.
Cystic Fibrosis: Symptoms and Signs
Cystic fibrosis does not feature with the same symptoms and sings in all patients. The actual problem which is associated with symptoms and signs of the disease is abnormal production of mucus and sweat glands. In people suffering from cystic fibrosis the sweat is much richer in salt comparing to healthy people. This may cause imbalance of electrolyte in the body and resulting symptoms. Furthermore, mucus in people suffering from cystic fibrosis is very thick and sticky. It tends to accumulate in the pancreas and in lungs. This eventually leads to malnutrition, improper growth and development in children, frequent respiratory infections and subsequent breathing difficulties and in some cases permanent lung damage.
People suffering from cystic fibrosis may also suffer from additional problems such as sinusitis, nasal polyps, clubbing, pneumothorax, hemoptysis, cor pulmonale, chronic abdominal pain and discomfort, bloating and rectal prolapse. Furthermore, these patients are at higher risk for liver disease, diabetes and gallstones.
Diagnosing Cystic Fibrosis
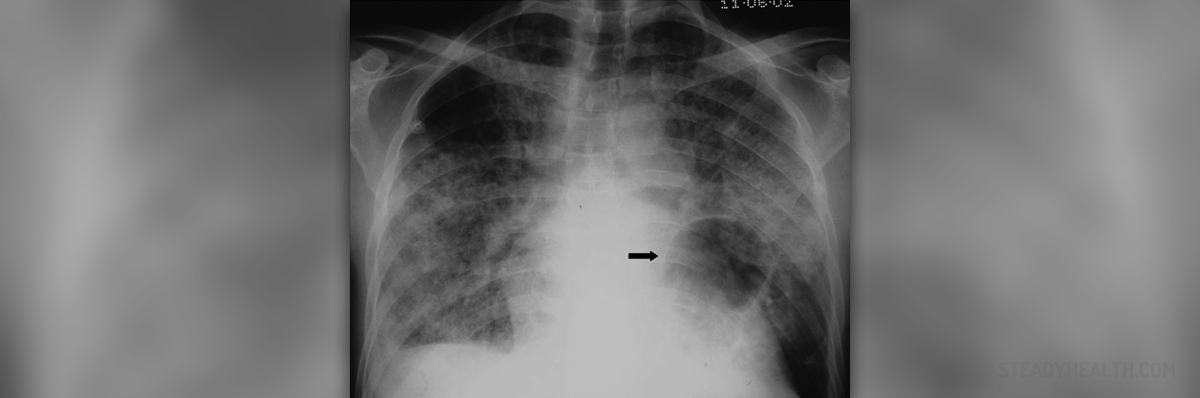
After thorough physical examination, certain blood tests and chest X ray, patients undergo a specific test called the sweat test. This test measures the amount of salt in one's sweat. The sweat is usually collected from the forearm. Increased amount of sodium chloride points to the presence of cystic fibrosis. There is one more test that can confirm the disease. It is called the immunoreactive trypsinogen test (IRT) and it is generally applied in newborns that tend not to produce enough sweat which is necessary for the sweat test.
Cystic Fibrosis: Treatment
Since cystic fibrosis belongs to genetic illnesses there is no cure. However, there are many treatments that may help patients and prolong their life spans.
It is essential to treat symptoms, infections, digestive problems and all other problems related to the disease. Infections are generally treated with antibiotics. Certain treatment may provide with elimination of stick mucus from the lungs and this way prevents recurrent lung infection. If cystic fibrosis leads to severe damage to the lung s a person may require lung transplantation.
Patients suffering from lung problems may benefit from physical therapy and exercises which help them with elimination of thick and sticky mucus. Breathing can be improved with bronchodilatators, mucolytics and decongestants.
Treatment for digestive problems includes a well-balanced and high-caloric diet (low in fat and high in protein). Some patients require pancreatic enzymes. And finally, vitamin supplements such as vitamin A, D, E and K may be prescribed as well.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...