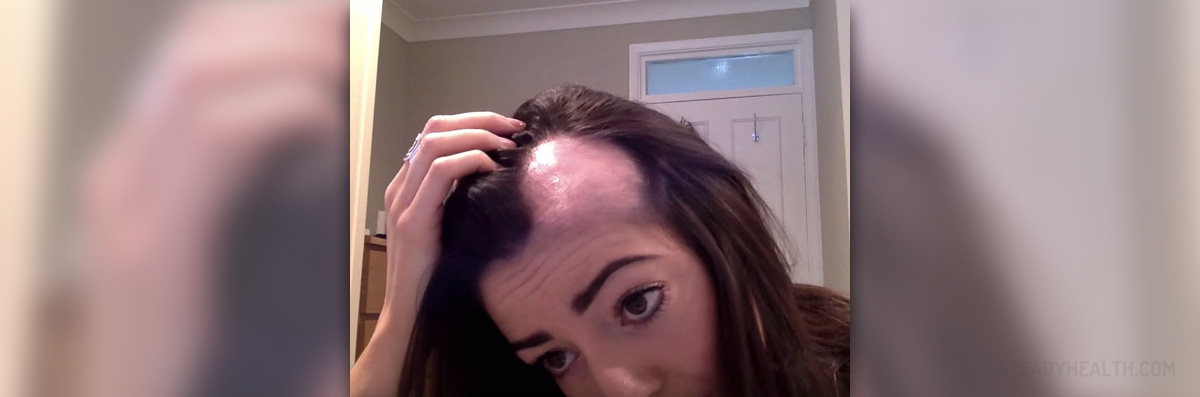
Scarring alopecia represents a group of rather rare disorders in which the loss of hair is accompanied by scarring of the affected skin. The disease leads to complete destruction of hair follicles and the healthy tissue is replaced with scar tissue. This condition affects both men and women and it is responsible for 3% of all cases of hair loss.
Causes of Scarring Alopecia
Scarring alopecia can be classified into primary scarring alopecia and secondary scarring alopecia.
In case of primary scarring alopecia the hair follicles are damaged by inflammatory processes which include accumulation of neutrophils and lymphocytes at the site of inflammation. Primary scarring alopecia is commonly associated with certain autoimmune illnesses such as systemic lupus erythematosus and scleroderma. There are several types of primary scarring alopecia and they feature with specific type of inflammatory cells involved in the very process of inflammation and consequent scarring. Scientists assume that the process of inflammation affects and destroys the stem cells and sebaceous glands which are located in the upper part of the hair follicle.
Secondary scarring alopecia is caused by burns, injuries and serious infections of the affected skin.
Apart from the previously mentioned scarring alopecia may be a consequence of certain chronic skin conditions such as lichen planus as well as granulomatous diseases. Furthermore, even aplasia cutis congenital, a most common congenital scarring alopecia, leads to permanent loss of hair. And finally, scarring alopecia is associated with folliculitis decalvans, inflammation of hair follicles and several more infections.
Symptoms of Scarring Alopecia
This condition typically features with gradual hair loss and scarring of the affected skin and it may or may not be accompanied by several more symptoms. If there are additional symptoms they include itching or burning sensations, redness of the affected skin, and in some cases, the skin may be covered with fluid filled blisters or pustules.
Diagnosis and Treatment for Scarring Alopecia
The diagnosis can be easily set due to typical symptoms and the presence of scar tissue. Still, the diagnosis must be confirmed by pathohistological examination of the biopted skin. This examination confirms the type of scarring alopecia and identifies the underlying cause.
The treatment for scarring alopecia basically depends on the underlying cause. In majority of cases it is treated with corticosteroids, especially if scarring alopecia occurs as a consequence of autoimmune diseases. Corticosteroids may be given in a form of creams or injections. Corticosteroids can be administered in a combination with isotretinoin and antibiotics.
In case scarring alopecia is caused by bacterial infection patients are prescribed antibiotics, and anti-fungal drugs are administered in fungal infections. Surgery is another option and finally, hair transplantation may help and improve the appearance of the scalp.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...