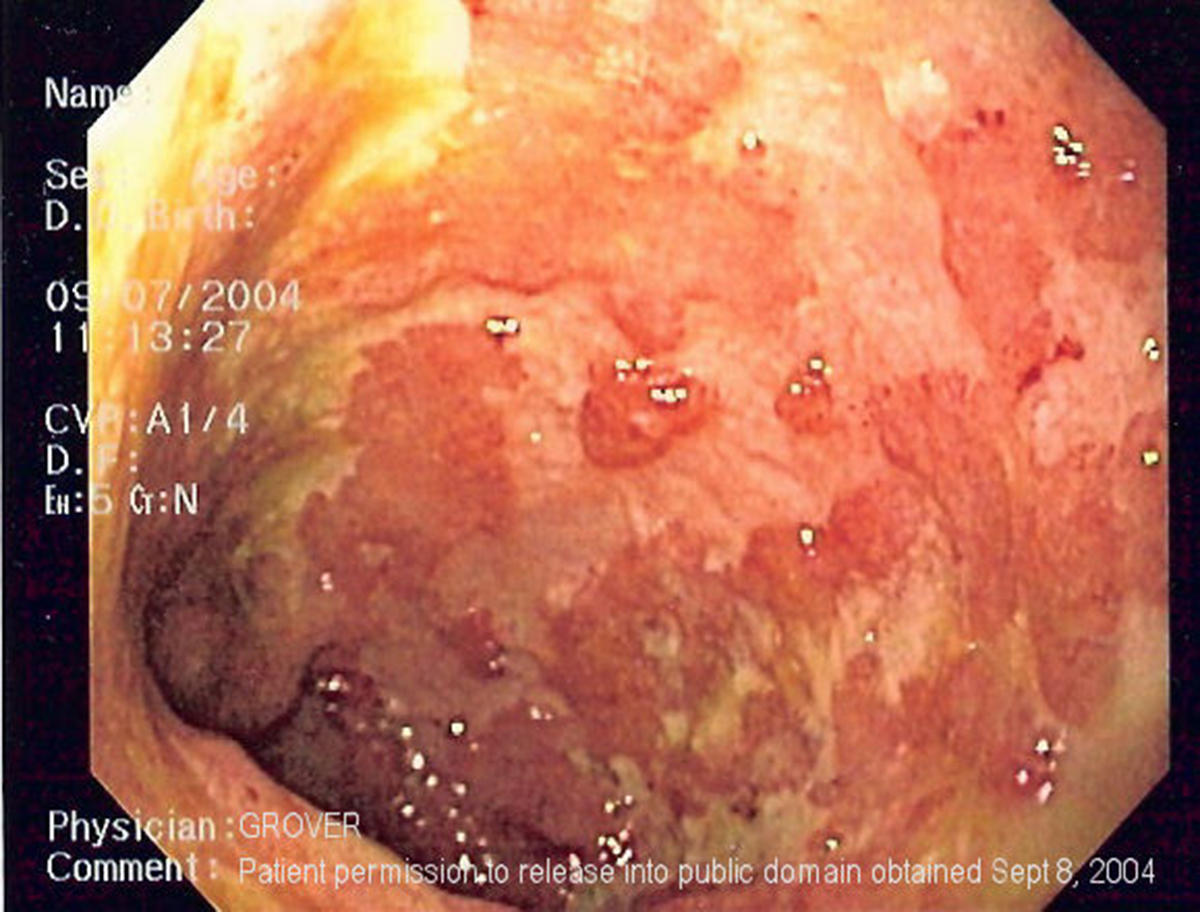
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory condition that affects the large intestine and rectum and features with abdominal pain and diarrhea. The inflammation generally affects only the innermost lining of the large intestine and rectum. It is not curable but it can be successfully brought under control with certain medications. The drugs can provide with a long-term remission. Clinical Characteristics of Ulcerative Colitis
The symptoms of ulcerative colitis generally vary according to the intensity and the very location of inflammation. The doctors usually classify colitis according to the affected part of the intestine.
Ulcerative proctitis represents inflammation of the rectum. It usually leads to bleeding (in many cases the only sign of ulcerative colitis). Additional symptoms of ulcerative proctitis include rectal pain, a feeling of urgency to move bowel or inability to move bowel even though there is an urge for defecation. This is relatively mild form of ulcerative colitis.
Proctosigmoiditis is an inflammation of both, the rectum and the colon and it leads to bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps and pain and painful sensations in the rectum associated with an urge to defecate even though the person cannot actually defecate (tenesmus).
Pancolitis represents an inflammation of the entire large intestine and it typically leads to bouts of bloody diarrhea, sever abdominal pain and cramps, fatigue and evident weight loss.
And finally, in case of fulminant colitis (a life-threatening form of the disease) the inflammation apart from intensive pain leads to profuse diarrhea, dehydration and shock. Fulminant ulcerative colitis may cause serious complications and colon rupture and megacolon are only some of them.
Causes of Ulcerative Colitis
Many researches used to believe that ulcerative colitis is associated with stress. Today, however, they are of different opinion. They believe there are other underlying causes of the condition and that stress may be considered only as one contributors of the disease. There seems to be a connection between improper functioning of the immune system and ulcerative colitis. Furthermore, some scientists say that the disease may be triggered by infective agents such as bacteria or viruses. Hereditary factors are also taken into consideration.
Treatment for Ulcerative Colitis
The goal of the treatment for ulcerative colitis is to reduce the inflammation and eliminate associated symptoms and signs. Ulcerative colitis can be brought under control by many medications. The first line therapy includes anti-inflammatory drugs such as sulfasalazine, Mesalamine, balsalazide and olsalazine. Furthermore, patients may be prescribed corticosteroids. In case such treatment does not provide with desirable results the doctors may opt for immune system suppressors such as azathioprime, Cyclosporine and infiximab. Apart from the mentioned some patients may benefit from nicotine patches. Symptomatic treatment includes antibiotics, anti-diarrheals, pain-relievers and iron supplements. Surgery is performed only in case of severe damage to the colon and in case of complications of the disease.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...