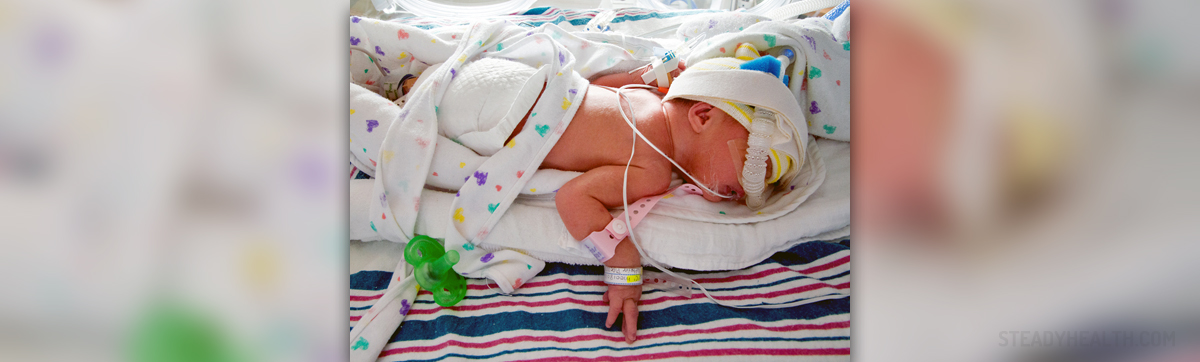
Chest Congestion in Infants and Common Causes
Chest congestion is a symptom of many illnesses that affect lower respiratory tract. The problem may also develop as a consequence of upper respiratory track illnesses. In this case the infection either spreads to lower portions of the respiratory tract or the mucus secreted from the upper respiratory tract drips down to the lungs.
Chest congestion represents the accumulation of excess fluid and mucus in the lungs. It does not have to affect all infants suffering from respiratory infections but it occurs frequently. The accumulation of fluids and mucus induces cough, chest pain and breathing difficulties. In case of severe chest congestion auscultation of the lungs reveals crackling sounds. If accumulation of fluid and mucus is extensive the child is suffering from severe breathing difficulties. It is essential to treat underlying condition and additional help in alleviation of chest congestion is achieved by specific medications.
Chest congestion in infants develops as a consequence of different respiratory infections including viral, bacterial and fungal infections. Some of the conditions that cause chest congestion include common cold, allergies, pneumonia, bronchitis etc.
Medicamentous Treatment for Chest Congestion in Infants
The child suffering from chest congestion must be immediately taken to the doctor. In majority of cases the child stays in hospital. The doctor performs physical examination, investigates patient's medical history and performs additional tests and exams such as chest X ray and certain laboratory tests. If the breathing is not adequate saturation of oxygen drops below 95%.
The goal of the treatment is to eliminate fluid and mucus from the respiratory tract and maintain optimal levels of oxygen. A well experienced pediatrician chooses the most convenient combination of medications in order to treat both, the underlying condition and consequent chest congestion.
Home Treatment for Chest Congestion in Infants
In case congestion is not severe and the symptoms and signs are not so intensive the child is sent home with prescribed medications and only in case symptoms progress and become worse the child is supposed to come back to the hospital.
Proper hydration is essential for clearing fluid and thinning out the mucus. Additional help is obtained from a cool mist humidifier. This device will prevent drying of the airways and the child will breathe much easily. And finally, the child is supposed to sleep in a bit elevated position. This way the intake of oxygen is improved and the cough may subside. After all the symptoms and signs withdraw the child must be taken for a check-up.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...