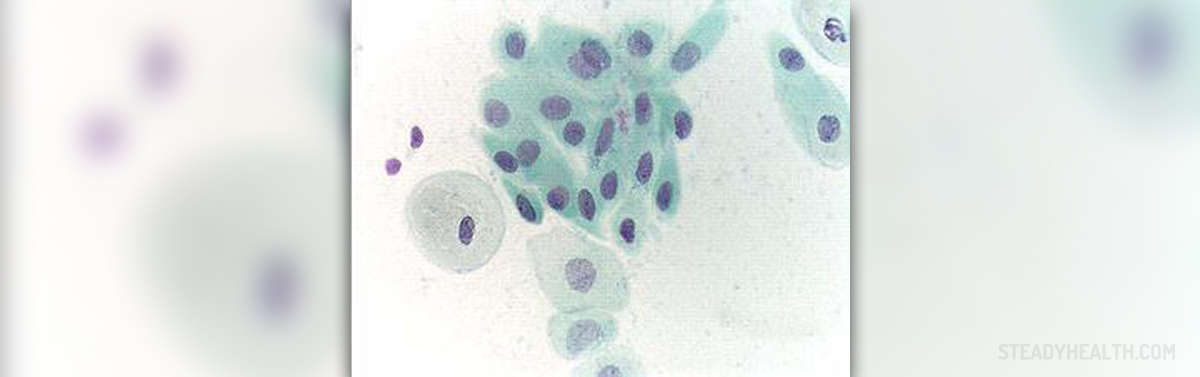
What Is A Pap Test?
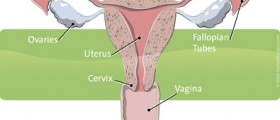
A Pap test is a simple and painless invasive test administered by a gynecologist to look for any changes on the cervix that might lead to infertility or tumor. It is recommended that every sexually active woman has a Pap test once a year while those who are inactive do not need to go more than once every two years. In Australia, regular Pap tests save over 1, 000 lives annually by catching and treating the changes before cancerous cells start to develop.Cervical Cancer
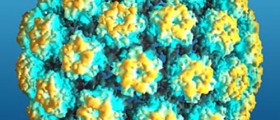
Cervical cancer is one of the most common types of cancers in women and it is in most cases caused by the HPV virus that is transmitted sexually. Nowadays, so many women get infected with the virus that clinicians consider it a regular part of being sexually active. In the United States 4 out of 5 women contract HPV at some point during their lives. It should be noted that, although primarily a sexually transmitted disease, it is possible to get HPV by coming into close contact with contaminated blood or bodily fluids. Further, in its early stages HPV generates little to no symptoms and it is therefore crucial to have screening tests every once in a while. In most cases HPV does not lead to cancer and it often remains in the body for a couple of years before naturally disappearing.Pap Smear Basic Instructions
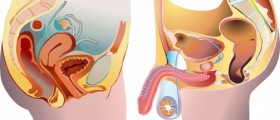
Pap test can be performed by a primary health care provider, a trained nurse, or by a gynecologist. In order to see the cervix a metal instrument is inserted into the vagina and the cervix is brushed gently to collect a sample. The cells are then sent to a lab and the results come back within a week. The test is painless but also slightly uncomfortable. When it comes to results, they either show significant, slight, or no changes at all compared to normal cells. Cervical cancer usually takes a few years to develop so individuals who have Pap tests once a year often have negative results. In cases in which the results show abnormalities more Pap tests will be administered over a short period of time. There are instances in which the malfunctioning cells disappear on their own and are just monitored periodically. Additional pap tests will show if the cells don’t go away, and the next step in the diagnostic process includes a colposcopy at a gynecologist’s office. The instrument that is again inserted into the vagina provides a better view of the cervix and the extent of changes. The doctor then recommends an adequate kind of treatment and the problem is often solved without any consequences for the health. If the colposcopy does not reveal anything significant a small tissue sample is taken from the cervix and sent to check for pathological changes. If there are abnormal cells on the cervix they will be surgically removed. Most gynecologists will use laser treatment to take out the damaged cells and any tissue that may be infected. The laser treatment is in most cases relatively painless and only local anesthetics are administered as needed. In addition, there are instances in which the results come back without any information due to the fact that the sample was unsatisfactory. If a small number of cells was collected or the cells are hidden by the mucus or blood the test will have to be repeated. It should be noted that even women who have been vaccinated again an HPV virus need to have regular Pap tests. Women who have gone through menopause and lost their periods should still get Pap tests whereas seniors over 65 can stop after 3 consecutive normal results. Lastly, women who have had their uterus removed need to consult with the primary health care provider whether regular Pap tests are necessary. If the uterus was not removed due to cancer Pap tests are probably nonessential. On the other hand, if the uterus was removed due to cancer regular gynecological checkups are critical for prevention of further spreading.Risk Factors And Prevention
Engaging in sexual intercourse with multiple partners increases the changes of contracting the HPV and in turn getting cervical cancers. Other significant risk factors include becoming sexually active before the age of 18 and contracting other sexually transmitted diseases and not treating them. In addition, individuals should be aware of the rules for getting the most accurate Pap test results. It is recommended that tampons, vaginal creams, or medicines not be used at least 2 days before the test. Also, having sexual relations 48 hours prior to the test should be avoided. Getting false Pap test results increases the likelihood for developing cervical cancer. Lastly, Pap tests are not performed if the patient is menstruating. The best results are obtained between the 10th and 20th day after the first day of the last period.


_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...